Become A Learning Development Specialist: Your Path to Shaping Tomorrow’s Talent
Become A Learning Development Specialist: Your Path to Shaping Tomorrow’s Talent
The Learning Development Specialist is the architect of human potential—designing, delivering, and refining transformative educational experiences that empower individuals and organizations. As industries evolve and knowledge becomes the core currency of competitiveness, this role stands at the intersection of pedagogy, technology, and strategic growth. This article unveils the comprehensive career path of a learning development specialist: the essential steps, attributes, and opportunities that define success in shaping modern learning ecosystems.
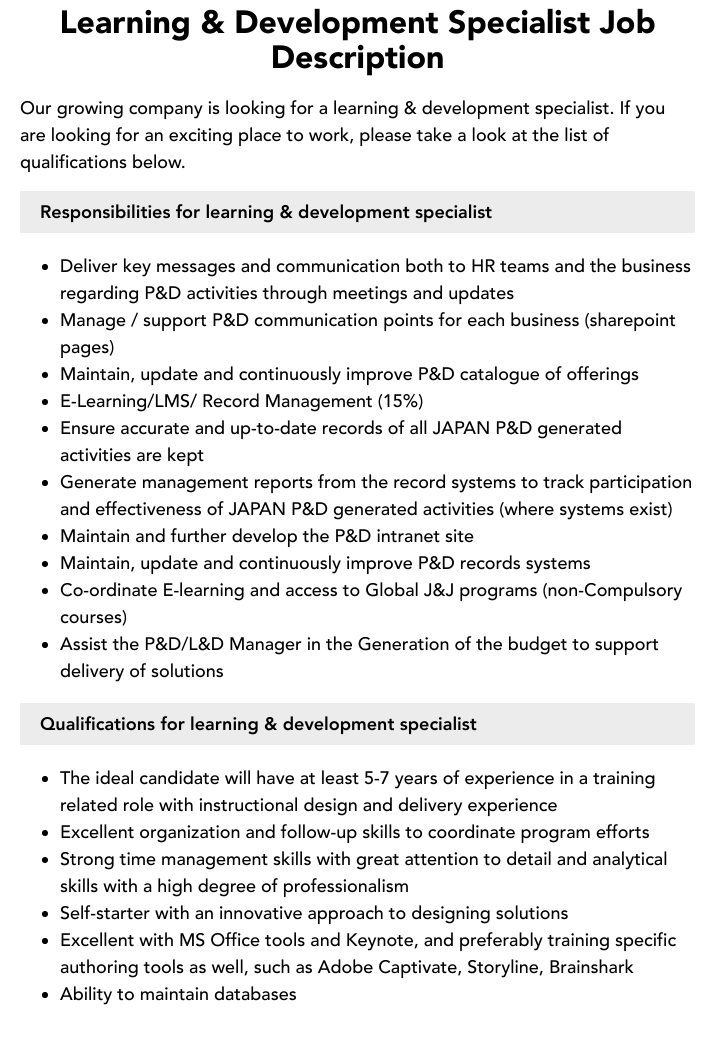
Understanding the Role: What Learning Development Specialists Do Daily Learning Development Specialists are more than instructional designers—they are curriculum engineers, instructional technologists, and change facilitators. Daily responsibilities often include: - Assessing organizational training needs and aligning programs with business goals - Collaborating with stakeholders to create engaging, measurable learning solutions - Integrating digital platforms, adaptive learning tools, and blended modalities - Launching pilot programs and analyzing performance data to refine content - Partnering with educators and leadership to foster a culture of continuous improvement As Karen Thompson, Senior Learning Strategist at a global ed-tech firm, notes: “We don’t just build courses—we build systems that scale learning across hierarchies and geographies.” This systems thinking defines the modern specialist’s core competency: translating abstract learning outcomes into practical, scalable impact. Core Competencies That Drive Success Success in this field hinges on a blend of technical knowledge, interpersonal insight, and strategic agility.
Key competencies include: - **Instructional Design Expertise**: Proficiency in frameworks like ADDIE, Bloom’s Taxonomy, and microlearning principles enables specialists to create structured, learner-centered content. - **Technology Savviness**: Comfort with Learning Management Systems (LMS), authoring tools, and emerging edtech such as AI-driven personalization engines is nonnegotiable. - **Data-Driven Decision Making**: Ability to interpret learning analytics helps specialists identify gaps, validate program efficacy, and justify investment.
- **Communication & Collaboration**: Working across departments—from HR to C-suite—requires clarity in translating educational theory into business results. The demand for these skills is growing rapidly. A 2023 report by the International Society for Performance Improvement estimates a 27% increase in roles tied to workforce learning by 2030, fueled by digital transformation and lifelong learning mandates.
Educational backgrounds vary but share a foundational strength in human-centered learning. Most specialists begin with a bachelor’s degree in education, instructional design, psychology, or organizational development. Advanced practice often demands postgraduate credentials such as a Master’s in Instructional Design or Educational Technology.
Optional but beneficial certifications—like Certified Professional in Learning & Performance (CPLP) or Microsoft Certified: Learning Solutions Architect—strengthen technical credibility. “While formal education provides the framework, real mastery comes from iterative practice,” says Dr. Marcus Liu, a learning development expert with over a decade of experience.
“The best specialists are perpetual learners themselves, staying ahead of trends in cognitive science, remote engagement, and inclusive design.” Career Trajectory and Progression The career path of a learning development specialist unfolds in distinct, yet flexible, phases. Entry-level roles typically center on tactical execution—developing training modules, managing LMS platforms, and supporting rollout coordination. With experience, professionals transition into specialized positions, such as curriculum lead or training program manager, overseeing end-to-end development and strategic alignment.
Senior specialists often assume roles resembling instructional architects or learning innovation leads, shaping enterprise-wide learning frameworks and mentoring junior teams. Many progress toward executive or advisory positions, influencing organizational culture, learning strategy, and performance outcomes at leadership levels. “Career growth mirrors the very principles we teach: learner-centricity, adaptability, and continuous evolution,” notes Elena Ruiz, now a director of learning transformation at a Fortune 500 corporation.
“Top performers don’t just master techniques—they become catalysts for systemic change.” Building a Competitive Edge In a competitive job market, differentiation comes through targeted skill development, visible impact, and strategic visibility. Methods include: - Cultivating a portfolio with diversified project examples—ranging from gamified modules to data dashboards - Actively engaging with professional networks via LinkedIn, EDUCAUSE, and learning technology conferences - Demonstrating fluency in emerging trends: AI-augmented learning, neuro-education, and inclusive design for neurodiversity - Fostering thought leadership through blogs, webinars, or open-source contributions to the learning community Specialists who align their growth with organizational priorities—such as upskilling for digital transformation or improving DEI outcomes—earn recognition as indispensable assets. Tools and Technologies: Powering Modern Learning Today’s learning development specialists wield an evolving toolkit.
Core technologies include: - **Learning Management Systems (LMS)**: Platforms like Docebo, Cornerstone, and Docebo shape how content is delivered and tracked. - **Authoring Tools**: Advanced software such as Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, and H5P enable engaging, responsive e-learning. - **Data Analytics Platforms**: Learning Analytics and Business Intelligence tools help correlate training inputs with business KPIs.
- **AI and Automation**: Chatbots, adaptive learning engines, and recommendation algorithms personalize learning journeys at scale. Integration of these tools requires not just technical proficiency but a learner-first mindset—ensuring technology enhances, rather than hinders, engagement and comprehension. Challenges and How to Overcome Them The path is not without hurdles.
Common challenges include: - Translating enterprise constraints into engaging content - Balancing speed of development with quality and accessibility - Gaining stakeholder buy-in in organizations resistant to change - Keeping pace with rapid technological shifts Strategies to navigate these include: - Partnering early with subject matter experts and learners to co-design solutions - Adopting agile methodologies for iterative, feedback-driven development - Advocating for inclusive design principles to ensure equitable access - Building persuasive business cases using metrics like knowledge retention and performance improvement “Every challenge is an opportunity to refine your approach,” advises Thompson. “The biggest reward comes not from avoiding obstacles, but from building resilience that transforms limitations into catalysts for innovation.” Industry Demand and Global Perspectives While demand is strongest in sectors undergoing digital transformation—technology, healthcare, finance, and education—learning development specialists are in growth across public and private organizations worldwide. Regions like North America, Western Europe, and Southeast Asia lead in investment, but emerging markets increasingly prioritize learning infrastructure, creating promising career frontiers.
Global Employer Expectations Employers seek professionals who understand cross-cultural learning needs, regulatory frameworks, and local relevance. Specialists must carefully balance standardized content with culturally responsive adaptations—ensuring training resonates across diverse audiences. Emerging Trends Shaping the Future Looking ahead, three trends are redefining learning development: 1.
**Lifelong Learning Ecosystems**: Organizations shift from one-off training to continuous, personalized learning paths enabled by AI and analytics. 2. **Immersive Technologies**: VR and AR create experiential learning environments for high-stakes skill development.
3. **Micro-Credentialing**: Bite-sized certifications and digital badges drive learner motivation and stackable career progression. Mastery of these domains positions specialists not just to keep up with change—but to lead it.
Final Thoughts: A Rewarding, Future-Proof Career The journey to becoming a Learning Development Specialist blends passion for human growth with strategic innovation. It demands continuous learning, adaptability, and a commitment to measuring real impact. For those driven by the belief that education transforms lives and organizations, this career offers both purpose and opportunity.



Related Post

Boca vs Union: A Defining Clash in Argentine Football’s Emotional Calculus

Lexi Schiff An Icon in Her Own Right: The Enigmatic Journey of Carol Arna, a Star Forged in Ambition and Mystery

Charlie Kirk’s Unflinching Voice on Gun Violence: An Unrelenting Call for Change

Pinellas County Inmate Search: How to Track Down Who’s Behind Bars Across Tampa Bay

