Center of Global Power: The FBI, CIA, KGB, CNN, IBM, and UCC — How Intelligence, Media, Tech, and Security Shape Global Influence
Center of Global Power: The FBI, CIA, KGB, CNN, IBM, and UCC — How Intelligence, Media, Tech, and Security Shape Global Influence
In an era defined by digital warfare, surveillance, and information dominance, the FBI, CIA, KGB, CNN, IBM, and UCC represent pivotal forces in shaping global power dynamics—each wielding influence across intelligence, media, technology, and national security. These institutions, though distinct in origin and mandate, converge in their impact on modern geopolitics, cybersecurity, public perception, and corporate decision-making. Their interplay reveals a complex ecosystem where state authority, corporate innovation, and real-time intelligence converge to define global stability and conflict.1
The Global Intelligence Juggernauts: FBI and CIA in Counterintelligence and National Defense
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) stand at the apex of U.S.
national security. The FBI’s domestic mandate focuses on counterintelligence, counterterrorism, and cybercrime, operating as both law enforcement and intelligence agency. Its Counterintelligence Division, often ranked among the most effective in the world, disrupts foreign espionage activities like those allegedly conducted by the Russian SVR and Chinese MSS.2 Meanwhile, the CIA specializes in overseas intelligence gathering, covert operations, and strategic analysis to support foreign policy and military decisions.
Both agencies share a legal framework rooted in constitutional authority: the FBI under domestic law, the CIA under the National Security Act of 1947. Their collaboration intensified after 9/11, marked by joint task forces and shared databases to counter transnational threats.3
Breaking Dossiers: From Surveillance to Strategic Insight
While the CIA excels in global signals intelligence (SIGINT) and human sources (HUMINT) far beyond U.S. borders, the FBI’s strength lies in legal domestic collection and cyber defense.
Both agencies battle complex threats like Russian election interference, Iranian cyberattacks, and North Korean espionage. In 2021, the FBI’s West antebellum-style cyber division disrupted a massive ransomware network traced to North Korea, showcasing how traditional law enforcement adapts to digital-age warfare.4 The CIA, conversely, leads in strategic forecasting—forecasting geopolitical shifts and assessing adversary capabilities, such as evaluating China’s expanding military modernization in the South China Sea.5
Media Power and Operational Influence: CNN’s Role in Shaping Global Narratives
CNN, a global media leader, transcends pure news delivery by influencing public opinion and, indirectly, policy decisions. Its 24/7 international reporting shapes perception during crises—from Middle East conflicts to climate diplomacy.
The network’s on-the-ground coverage often becomes a vital intelligence feed, though it walks a line between journalism and strategic influence. During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, CNN’s real-time reporting where few other outlets operated amplified criticism of Moscow while spotlighting Ukrainian resilience.6 Though not an intelligence entity, CNN’s capacity to steer narratives places it in the broader ecosystem of information power—where perception equals influence.
CNN’s Embedded Stories: When Journalism Meets Strategy
Journalistic coverage by CNN does more than inform—it can alter diplomatic calculus.
The network’s exclusive interviews and live battlefield reports serve as soft power tools, amplifying Western perspectives and exposing human rights abuses. In 2023, its investigative series on China’s Uyghur detention camps pressured multinational corporations to reassess supply chain risks, linking media exposure directly to economic decisions. This media-intelligence feedback loop demonstrates how information dissemination drives both public awareness and corporate risk management.
Tech Giants as Security Architects: IBM’s Cybersecurity Leadership
In the cyber domain, IBM stands as a pivotal corporate actor whose technologies underpin global defense networks. As a leader in enterprise cybersecurity, IBM develops AI-driven threat detection systems and blockchain-based data integrity solutions used by governments and major institutions. Its X-Force threat intelligence unit analyzes millions of attack vectors annually, helping shape proactive cyber defense strategies.7 Operating at the intersection of private innovation and national security, IBM’s tools are embedded in critical infrastructure—from power grids to defense communication systems—making it a silent guardian of digital stability.8
The IBM Edge: From Secure Clouds to AI-Driven Defense
IBM’s cloud security platform integrates zero-trust architectures and automated incident response, reducing breach response times by up to 70% according to industry benchmarks.9 By partnering with agencies like the NSA and Department of Defense, IBM bridges corporate agility with federal security priorities.
Its Watson AI platform, repurposed for cyber threat hunting, identifies patterns in vast data streams, enabling anticipatory defense beyond traditional reactive models.
State Majesty and Covert Reach: The KGB’s Legacy in Modern Intelligence Dynamics
The Russian state’s Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), once known as the KGB’s direct successor, remains a central player in global espionage, disinformation, and asymmetric warfare. The SVR’s operations target Western democracies through cyber intrusions, propaganda campaigns, and influence operations—tools designed to erode trust in institutions and amplify division.10 Its alleged interference in the 2016 U.S.
election and cyberattacks on Western critical infrastructure epitomize hybrid warfare strategies that blend intelligence, media manipulation, and cyber sabotage.11
SVR’s Hybrid Toolkit: Disinformation, Hacking, and Influence War
SVR’s methods reflect a 21st-century intelligence paradigm: blend traditional espionage with digital operations. It deploys troll networks on social media platforms to spread divisive content, while domestically and abroad, its agents infiltrate political discourse, scientific research, and diplomatic channels. In tandem, SVR leverages Russian state media and private firms to amplify narratives—creating a layered assault on democratic resilience.
Its cyber units conduct espionage and sabotage, such as the 2020 SolarWinds breach attributed to Russian mercenaries linked to SVR-linked groups.12
Intelligence Collaboration and Corporate Stewardship in the Security Ecosystem
While often perceived as rivals—state agencies versus media conglomerates, corporations versus state services—the FBI, CIA, KGB, CNN, IBM, and UCC alike form an interdependent global security ecosystem. The FBI and CIA coordinate cyber defense against foreign threats with private sector leaders like IBM, leveraging corporate innovation to protect national interests. Meanwhile, UCC and similar defense integrators—specializing in secure communications, electronic warfare, and AI analytics—supplement official capabilities with cutting-edge tech applied to battlefield and diplomatic scenarios.13 IBM’s robust threat intelligence feeds operational planning for agencies monitoring cyber warfare trends, while UCC develops secure platforms enabling encrypted coordination among allied forces.
6 Pillars of Modern Intrigue: Intelligence, Media, Tech, and Corporate Stewardship
- The FBI’s cyber units and CIA’s global HUMINT networks provide foundational defense against espionage and cyberattacks.
- CNN’s global reach shapes public perception, influencing both diplomatic outcomes and domestic trust in institutions.
- IBM delivers enterprise-grade cybersecurity and AI tools that strengthen digital resilience across governments and corporations.
- UCC and tracking entities build secure communication and electronic warfare systems integral to modern defense architectures.
- SVR exemplifies state-sponsored influence operations using disinformation and cyber intrusions to undermine democratic governance.
- Interagency and corporate partnerships create a multi-layered defense infrastructure adapting to evolving threats.
This fusion of intelligence rigor, media power, technological prowess, and corporate expertise defines the contemporary battleground—not just for territory, but for truth, data, and influence. As hybrid threats grow more sophisticated, the synergy between these entities grows essential to preserving national and global stability in an increasingly fragile digital age.
The Future of Power: Where Intelligence, Media, and Technology Converge
The landscape of global power is no longer shaped by armies alone.
Instead, national security hinges on the seamless integration of intelligence capabilities, media influence, corporate cyber innovation, and corporate defense infrastructure. The FBI, CIA, KGB, CNN, IBM, and UCC represent distinct but converging nodes in a network that defines modern statecraft—where data is strategic, perception is weaponized, and technology is both shield and sword. As geopolitical tensions intensify and cyber threats evolve, their coordinated—and often covert—actions will continue to shape the rules of engagement in the 21st century, for better or worse.
The future of global order rests not just in policy or weapons, but in the invisible architecture of surveillance, information, and innovation.14
The fusion of intelligence, media, tech, and corporate stewardship reveals a new paradigm: influence no longer emerges solely from force, but from control of information, perception, and digital frontiers. In this arena, each institution—each name mentioned—fuels a silent, global struggle for dominance, trust, and security. References:
FBI and CIA: Pillars of U.S.
Intelligence
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) form the backbone of U.S. national security, balancing domestic law enforcement with global counterintelligence. Both agencies collaborate closely, particularly in cyber defense against adversaries like Russia and China, integrating legal authority with clandestine operational capabilities.
Legacy of Espionage: From KGB to Modern SVR
The KGB’s transformation into today’s SVR maintains Russia’s legacy of sophisticated state espionage, combining traditional intelligence with hybrid warfare—cyber intrusion, disinformation, and covert influence operations targeting Western democracies.
CNN: Journalistic Power in Information War
CNN’s 24/7 coverage and global reach make it a critical node in real-time perception management, shaping public discourse and influencing diplomatic and military decision-making through instant, widespread narratives.
IBM as Cyber Defense Innovator
IBM leads enterprise cybersecurity with AI-driven threat detection and blockchain solutions, offering tools essential for protecting critical infrastructure and advancing national cyber resilience strategies.
SVR’s Hybrid Campaigns
The Russian SVR conducts layered influence operations blending disinformation, cyber intrusions, and proxy networks to destabilize democracies—a model of 21st-century hybrid warfare redefining global security threats.
Interdependence in Security Ecosystems
Modern security transcends institutional silos.
FBI and CIA coordinate with IBM’s tech innovations and UCC’s secure systems, illustrating how state and corporate forces jointly counter asymmetric threats through shared intelligence, cutting-edge tools, and layered defense strategies.
Shifting Power Dynamics
Power in the digital era emerges from control of information, technological superiority, and strategic alliances. The coordinated, often invisible actions of entities like the FBI, CIA, KGB, CNN, IBM, and UCC illustrate a complex, interdependent ecosystem defining the future of global stability.




Related Post

2023 Honda CR-V Hybrid AWD: Score Impressive MPG with Premium All-Wheel Drive Performance

Gypsy Rose’s Crime Scene: Decoding the Tragedy Behind the Gypsy Rose Mother Mystery

Affirmative Action: What You Need To Know—The Definitive Guide
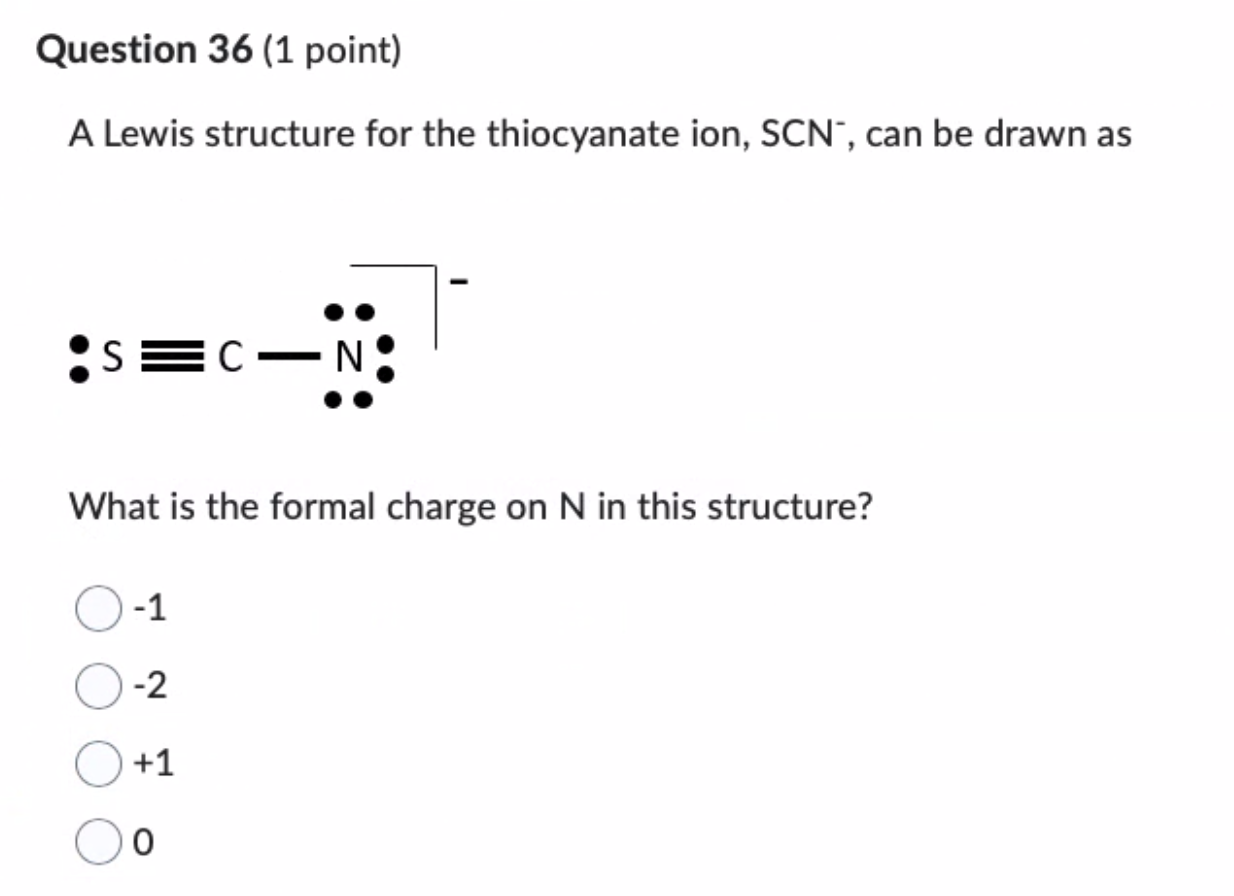
The Lewis Structure of SCN⁻: Decoding the Chemical Blueprint of a Versatile Ion
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(979x464:981x466)/zoe-kravitz-parents-main-3f61f9d60ae44860a7f8a2c8a7ba1973.jpg)
