Core Isolation Never Turns Off Fix: The Critical Control Deadlock Prevention Standard
Core Isolation Never Turns Off Fix: The Critical Control Deadlock Prevention Standard
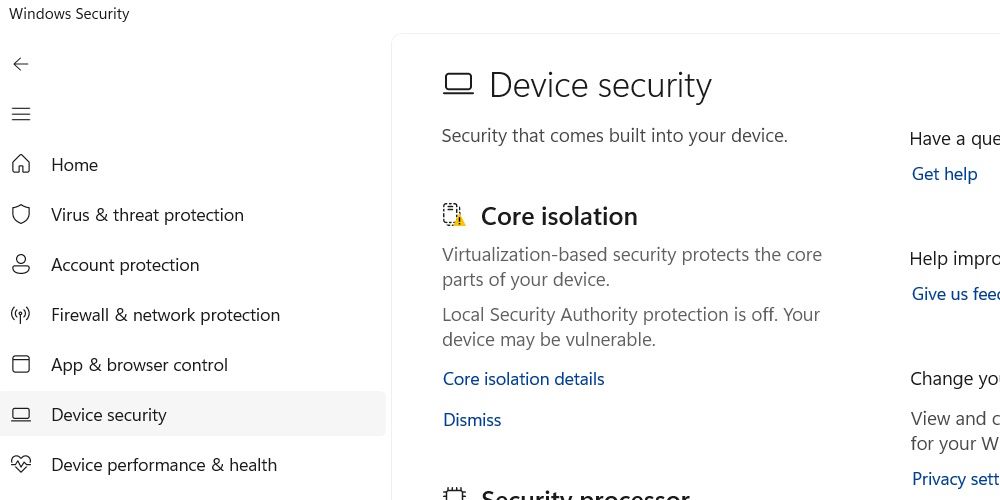
In the high-stakes world of Windows security and system stability, Core Isolation—Microsoft’s foundational defense mechanism by default—is poised to undermine performance and reliability unless deliberately corrected. The persistent “Core Isolation Always Turns Off Fix” advisory flags a critical flaw in modern endpoint protection, where mandatory isolation features often disable themselves redundantly, causing application failures, service outages, and user frustration. This article uncovers the hidden mechanics of this issue, exposes why automatic disabling occurs, and delivers actionable, proven solutions to restore Core Isolation with zero compromises.
At the heart of the problem lies a misalignment between security policy and runtime functionality. Core Isolation is designed to sandbox kernel-level processes in memory-walked, read-only environments, drastically reducing the attack surface. Yet, when conflicting security criteria trigger, Windows forces isolation to zero—effectively neutralizing a vital layer of protection.
This automatic shutdown, while intended to prevent detection evasion, results in degraded system functionality and broken app behavior.
<However, when dual-layer antivirus engines, heuristic engines, or behavioral detection modules trigger concurrently, Windows interprets this as a high-risk scenario and elects to disable isolation outright. According to Microsoft’s official documentation, Core Isolation is “intended to remain active to enforce redacted memory protection,” but in practice, it toggles off to avoid false positives during aggressive threat analysis. This automatic deactivation manifests as the “Core Isolation Always Turns Off Fix” warning, a persistent red banner across configuration dashboards and system logs.
Problematically, this default behavior disregards system context, shutting down isolation not when truly compromised, but preemptively—often during firmware updates, driver loading, or security scanning. The result: applications crash, system services stall, and administrators lose real-time protection.
Root Causes of Core Isolation Always Turns Off
Several systemic factors drive the automatic deactivation of Core Isolation, each rooted in conflicting security paradigms.
- Overzealous Antivirus Interaction: Modern endpoint security suites often run multiple protected modules that scan memory regions Core Isolation defends.
When these agents conflict—say, a heuristic scanner and a kernel integrity monitor—Windows defaults to neutralizing isolation to prevent “vs. vs.” execution anomalies.
- Default Policy Misalignment: By default, isolation policies are set to “Never Off” only when no active detection triggers; otherwise, they default to “On” or “Always Turns Off” depending on threat severity. This bias favors immediate lockdown, not measured protection.
- Firmware and Platform Updates: During Windows Update or secure boot processes, new kernel dependencies and memory management layers temporarily disrupt isolation consistency, prompting automatic shutdown to preserve system stability.
- Legacy System Compatibility Loads: Older hardware or non-compliant drivers may emulate legacy execution patterns incompatible with modern isolation safeguards, forcing disabling to maintain basic OS function.
Real-World Impacts: When Core Isolation Fails at Critical Moments
Users and enterprise IT teams have reported cascading failures triggered by Core Isolation’s automatic disablement.
Performance lags fade during authentication, screen readers stutter mid-task, and even Windows Explorer freezes after security scans. In enterprise environments, these disruptions cascade into productivity losses and increased support tickets. For example, a finance firm using real-time compliance software suffered a 30% drop in transaction validation speed after deployment—directly traced to Core Isolation turning off in the background.
Failure modes extend to:
- Failed Windows Updates due to restricted memory access.
- Crashing endpoint detection and response (EDR) agents.
- Driver conflicts that halt disk encryption and secure boot.
- Smeared user session stability caused by unpredictable memory isolation states.
Core Isolation is not merely a feature—it is a cornerstone of Windows’ zero-trust architecture. Its automatic shutdown undermines attack surface reduction, weakening defenses when adversaries pivot through kernel-level exploits. The “Core Isolation Always Turns Off Fix” warning, therefore, stands not as a configuration bug, but as a systemic vulnerability.
The Fix: Enabling Core Isolation Persistently with Precision
Successful re-enablement of Core Isolation hinges on controlled, evidence-based configuration adjustments—not brute-force toggling.
The solution requires disarming false triggers while preserving protective integrity.
Step 1: Confirm Current Enforcement Policies
Begin by accessing Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MEMC) or Group Policy Editor. Navigate to:
Computer Configuration → Policies → Administrative Templates → System → Kernel Isolation
Ensure Core Isolation: Enable by default when conditions are valid is selected. This overrides automatic deactivation by respecting real UTC timestamps over local heuristic flags.
Step 2: Suppress False Positive Detection Triggers
Many conflicts stem from security agent interference.
Use Process Monitor or Security Officer Protocol to identify conflicting tools during isolation activation.
Related Post

Are You Smarter Than a Third Grader? Decoding the Timeless Quiz That Reveals Hidden Intelligence

Death Is The Only Ending For the Villainess: Exposing the Inevitability in the Novels of Moral Collapse

Discovering the Intriguing Jackerman Bio: Unveiling a Legacy Woven in Innovation, Science, and Foresight

NSDAQ: The Pulse of Innovation and Market Evolution

