Divine Right Explained: The Unchallenged Power That Shaped Kings and Empires
Divine Right Explained: The Unchallenged Power That Shaped Kings and Empires
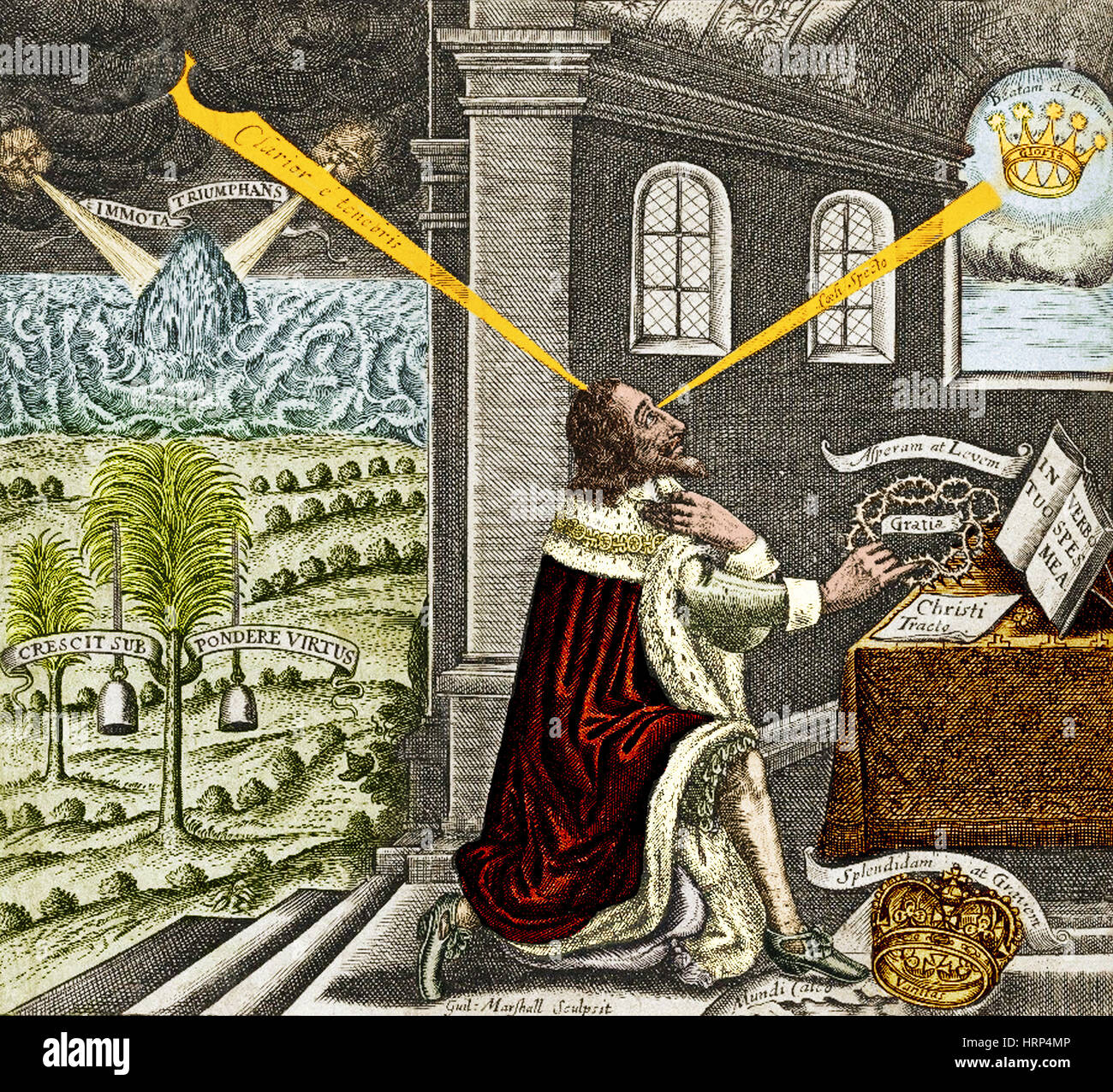
Though long superseded by modern governance, the principle of Divine Right—asserting that monarchs derive authority directly from God—once stood as the unshakable foundation of political legitimacy. This doctrine transformed rulers into sacred figures, elevating kingship beyond mere human institution and embedding divine sanction into the very fabric of legal and social order. Far more than mere religious metaphor, Divine Right served as a powerful political tool, justifying absolute power and quelling challenges to royal authority across centuries and continents.
The Theological Foundations of Divine Right
At its core, Divine Right rests on a theological premise: that God ordains the sovereign, making kings as much agents of divine will as mortal rulers.
This belief emerged prominently in medieval Europe but was later formalized in intellectual and legal arguments. As philosopher John Locke later critiqued, the idea held that a monarch’s power was not granted by people or treaties, but by a higher, immutable force. The assertion was simple yet totalizing: “To hinder the king is to oppose God’s law,” a sentiment echoed in royal proclamations throughout history.
This doctrine turned resistance not only as rebellion but as religious sin. The Decalogue-like moral weight behind the decree discouraged dissent, framing loyalty to the crown as a sacred duty. “The king is God’s lieutenants on earth,” declared Thomas Hobbes in Leviathan, “and therefore his decrees cannot be questioned without violating divine mandate.” Such language reinforced the sovereign’s infallibility, embedding religious validity into political obedience.
Political Implications: From Myth to Monumental Power
By vesting authority in divine will, rulers transformed political power into an unquestioned hierarchy that transcended earthly institutions. No parliament, council, or people-held veto—each challenge threatened both state and soul. The French monarchy under Louis XIV epitomized this: “L’État, c’est moi,” declaring that the king’s person and governance were one.
His absolute rule, sanctified by Divine Right, reshaped France’s administration, centralizing power like never before. In England, the doctrine reached its zenith during the 17th century, fueling the clash between monarchy and Parliament. King James I’s *The Trew Law of Free Monarchies* (1607) argued, “No subject has right to question the king’s decrees, for to question the king is to question God’s ordinance.” This reasoning underpinned the divine legitimacy of rulership, justifying absolute control and resisting early democratic movements.
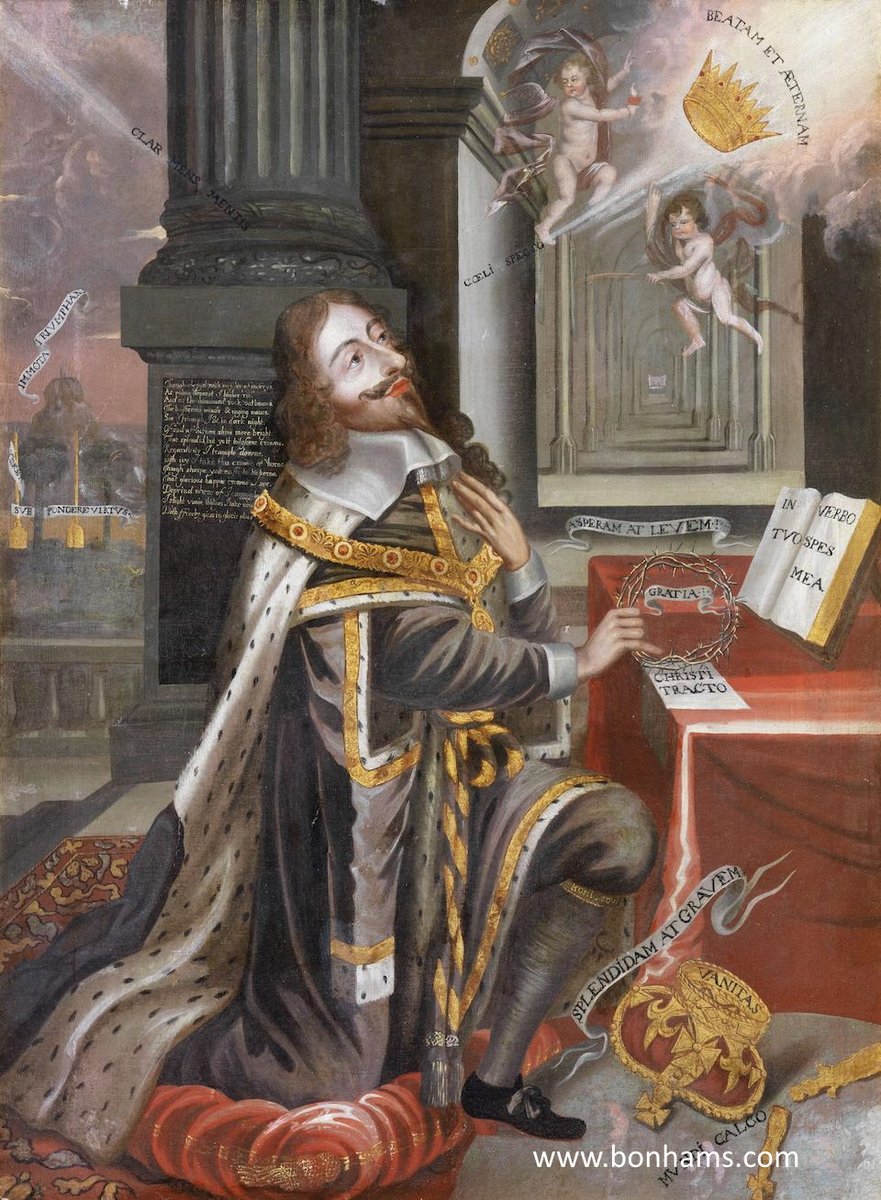
Yet, paradoxically, this absolute claim also provoked intense rebellion—most sharply in the English Civil War and the execution of Charles I in 1649.
Divine Right thus became both the crown’s greatest shield and its deadliest vulnerability. Where it succeeded, kings ruled unchallenged; where it faltered, civil war and revolution followed.
Global Variants: Divine Right Beyond Europe
Though often associated with European absolutism, the concept bore distinct forms across cultures.
In imperial China, the Mandate of Heaven bore philosophical rather than strictly theological overtones, asserting that rulers held legitimacy only as long as they governed justly—a conditional divine endorsement. Still, failure to govern morally risked losing heavenly favor, justifying rebellion, much like European precedents. In Japan, the emperor’s lineage was claimed as direct descent from Amaterasu, the sun goddess, anchoring sacred authority in mythic origin.
While political power shifted over centuries, the symbolic role of the emperor persisted, reflecting a divine undercurrent in governance far longer than in many Western systems.
The Undoing: Enlightenment, Revolutions, and the Decline
By the 18th century, Enlightenment thinkers dismantled the intellectual foundations of Divine Right. Voltaire, Locke, and Rousseau championed reason, natural rights, and popular sovereignty, undermining the claim that kings ruled by divine fiat alone.
The American and French Revolutions became landmarks in this intellectual shift—declarations of governments founded on consent, not divine decree. “Men are born free, and forever free,” proclaimed the French *Declaration of the Rights of Man*, directly contradicting the sacred status once assigned to monarchs. The worldwide rise of republics and constitutions marginalized Divine Right as an obsolete justification for unchecked power.
Yet, its legacy endures subtly: modern leadership often retains rituals and language that echo its sacred framing—oaths taken in God’s name, “divine mandate” in policy rhetoric, or the aura of irreplaceable leadership. While absolute monarchy has largely given way to checks and balances, the echo of Divine Right lingers in the conviction that true authority transcends mere law. It reminds us that power’s legitimacy is always contested—shaped as much by belief as by force.
Enduring Echo: Divine Right in Modern Governance
Though formal Divine Right is history’s relic, its conceptual framework continues to influence political discourse.
Leaders invoke unprecedented mandates, controversial referenda, or moral imperatives framed as “God-given tasks,” recalling the sacred legitimacy once reserved for kings. In democracies, the notion survives in how governing legitimacy is perceived—not just legally, but spiritually in collective purpose. Whether in constitutional oaths swearing “upon God,” or public debates on justice and duty, the doctrine’s shadow lingers.
Understanding Divine Right reveals more than a historical footnote; it illuminates the deep, enduring human impulse to anchor power in something higher than ourselves. In doing so, it reminds us that legitimacy endures not just in law books, but in the shared beliefs we hold sacred.



Related Post

Marion SC News: Your Local Updates Unveil Environmental Push, Broadband Expansions, and Economic Revitalization

Purina Ha Vegetarian: A Plant-Based Revolution in Pet Nutrition

Miranda Harts Husband: Behind the Laughter – A Deep Dive into a Private Life Shaped by Public Fame

Breaking Bad Profit: Unraveling The Financial Architecture of TV’s Most Lucrative Adventure

