Less Than vs Greater Than: Mastering Symbols That Shape Logical Thinking
Less Than vs Greater Than: Mastering Symbols That Shape Logical Thinking
From classroom classrooms to boardrooms, the symbols less than (<) and greater than (>), their counterparts less than or equal to (≤) and greater than or equal to (≥), quietly govern how we interpret relationships—between numbers, ideas, and even timelines. These humble punctuation-like symbols are foundational in mathematics, computer science, law, and everyday decision-making, yet their subtle distinctions often escape casual attention. Understanding their precise meanings prevents errors in reasoning and communication.
While often treated as interchangeable, each symbol carries a distinct implication—one a strict boundary, the other a flexible threshold.
At their core, the symbols less than (<) and greater than (>) define directed comparisons: a value A is strictly less than B, written as A < B, meaning A lies directly below B on a number line. By contrast, greater than (>), A > B, indicates A resides above B—no overlap, no equal.
But when equalness is included, the symbols expand: A ≤ B allows for a flat point of contact, embodying inclusion rather than strict superiority. This nuance is critical—"A is greater than or equal to B" permits equality, reshaping logical certainty.
The Precision of Direction in Symbolism
Every symbol tells a direction. The downstroke of < signals strict inferiority, leaving no room for equality.Consider place values: 5 < 10, a clear hierarchy—five cents is less than ten dollars. In mathematics, inequalities anchor scientific modeling: if T < 25°C, the temperature remains strictly below the threshold, not at it. Kitchen scales rely on this logic too—labeling a weighing function as ≤ 100g implies failure beyond that limit.
Conversely, the upward sweep of > marks superiority without hesitation. In programming, a conditional like if score > 90 confirms success with a sharp boundary. Olympics openings follow this rhythm: opening ceremonies rank nations > participating countries, emphasizing hierarchy.
When analyzing data trends, saying y > x at a pivot point reveals decisive upward momentum—your startup’s revenue, y = 250k, exceeds last quarter’s y = 220k, signaling growth. < **Key Definitions:** - < = A is strictly less than B (A < B), no equality allowed. - > = A is strictly greater than B (A > B), absence of equality.
- ≤ = A is less than or equal to B (A ≤ B), includes equality. - ≥ = A is greater than or equal to B (A ≥ B), includes equality. The strategic use of these symbols transforms abstract comparisons into actionable truths.
Whether aligning feedback on performance metrics or drafting legal clauses, clarity hinges on precision.
In standards and regulations, equality thresholds built from ≤ or ≥ carry real-world weight. For example, work permits often specify employment ≤ 20 hours per week, explicitly forbidding overtime—“less than or equal.”” States cap emissions at 50 tons, meaning “≤ 50 ppm” defines compliance, not just limits. Legal documents rely on this precision to avoid ambiguity: “a contract is void ≤ termination date” leaves no wiggle room.
Even inflation benchmarks use both forms—CPI trends indexed at <2.5% (<) or ≥3% (≥) directly impact monetary policy decisions.
Real-World Applications Beyond Numbers
Beyond mathematics, < and > shape communication design. In user interfaces, form validation leverages inequality checks: “Password must be >8 characters” ensures minimum strength.Accessibility guidelines cite ≥ 14pt font size as optimal—expressions like “≤ 18pt” define when text becomes visually constrained. In education, rubrics use ≤ maximum points for partial credit, ensuring scores reflect incremental mastery. Case Study: Supply Chain Logistics Consider inventory thresholds.
A warehouse holding ≤ 50 units is below safety stock—triggering restock protocols. Conversely, inventory ≥ 100 units triggers bulk pricing negotiations—both states governed by these symbols. Automation scripts parse real-time data: ``` if current_stock < threshold then reorder; if remaining_order > 0 then auto-ship; ``` This logic, embedded in ERP systems, minimizes waste and maximizes efficiency—proof of symbols’ quiet dominance in operational architecture.
In legal frameworks, equality’s inclusion alters consequences. “Agreements ≤ 30 days” permits early termination, whereas “agreements > 30 days” limit window for withdrawal. Contractual “minimums” (≥) and “maximums” (≤) govern pricing, compliance, and liability.
Courts interpret statutory limits through these lenses: a speed limit of 65 mph (<65) differs legally from “speed ≤ 65,” ensuring enforcement clarity.
Navigating the Logic of Limits and Thresholds
The symbolic distinction between less than, greater than, and their inclusive counterparts transcends notation—it defines how systems self-correct, communicate boundaries, and enforce fairness. Whether modeling climate thresholds (<25°C global average), evaluating student progress (<50%) or auditing financial disclosures, these symbols anchor certainty in an uncertain world.Misinterpretation invites mismanagement: mistaking ≤ for < might include compliant overload, while overlooking ≥ could allow regulatory breaches. Yet mastery unlocks clarity. Engineers, programmers, and policymakers alike rely on these tools to define targets, detect anomalies, and operationalize standards.
The next time you encounter a dashboard, contract, or live tweet citing a percentage, pause—double-check whether criteria hinge on equality or exclusivity. In doing so, you wield a silent but powerful instrument of precision.
Less than and greater than are not mere punctuation but cornerstones of structured thought.
Their inclusion or omission shapes outcomes, decisions, and systems—making silent comprehension profoundly impactful. Understanding their logic isn’t just academic; it’s essential for clear, confident navigation through data, rules, and reality itself.
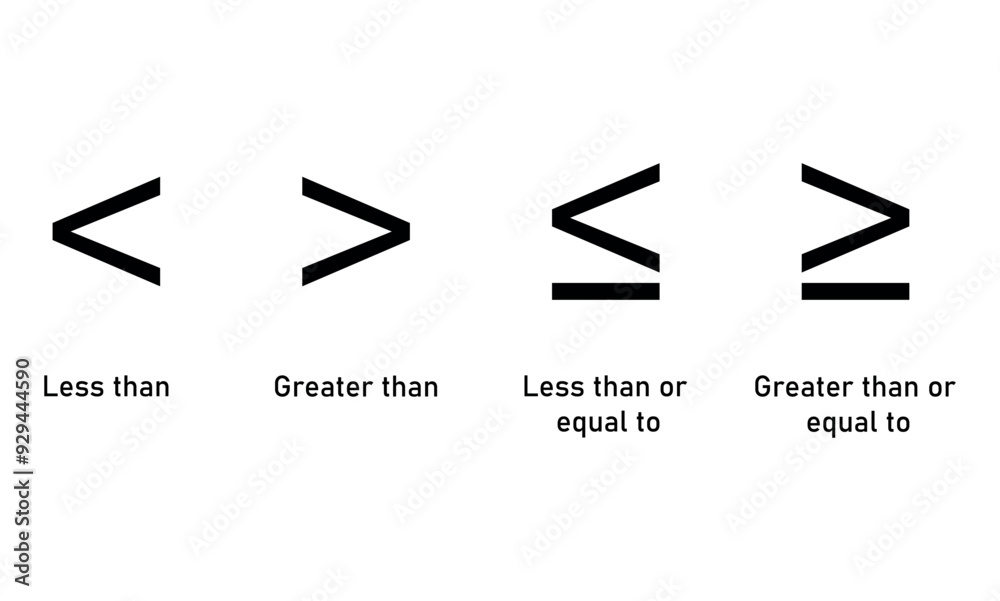



Related Post

Netflix’s Carbon Leap: How Streaming Giants Are Reshaping Global Sustainability

The Ultimate Guide to the 'Good Burger' Movie Cast
Exploring The World Of 1Tamilblasters: A Comprehensive Guide to Tamil Blasting Culture and Technology

Who Is Big Mike Obama? The Enigmatic Figure Behind The Controversy

