Li Molar Mass: The Molecular Weapon Behind Chemistry’s Most Crucial Calculations
Li Molar Mass: The Molecular Weapon Behind Chemistry’s Most Crucial Calculations
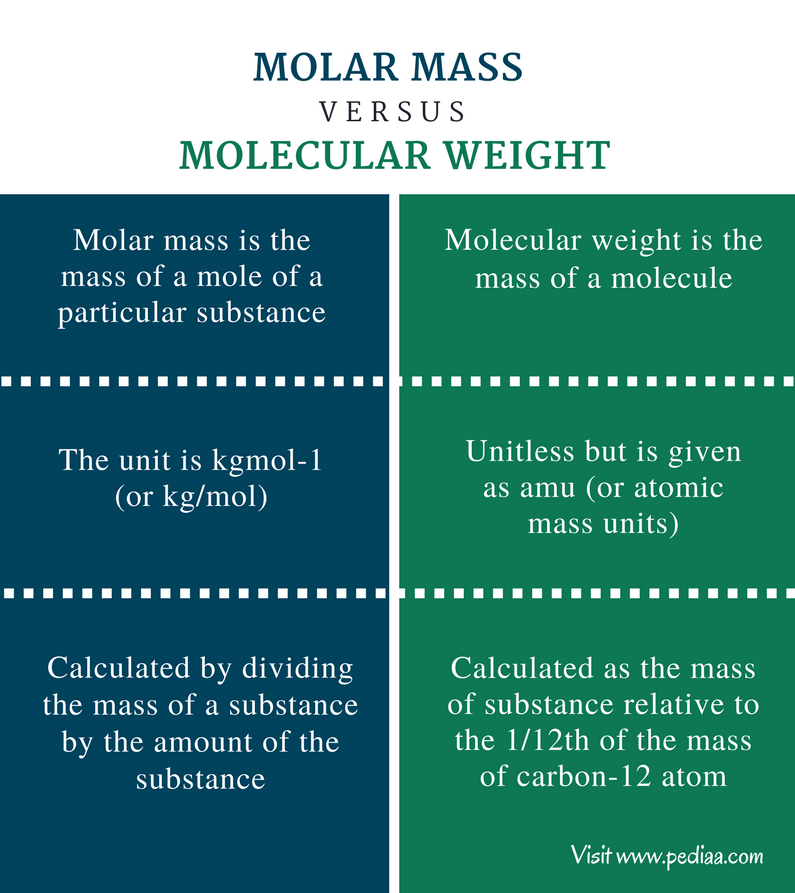
At the heart of chemical analysis lies the precise and indispensable concept of molar mass—the foundation for understanding every molecular interaction, reaction stoichiometry, and industrial process. Among the wide array of elements and compounds measured in chemistry, Li’s molar mass stands out not just for its value, but for its profound implications in both academic research and real-world applications. From predicting reactivity trends in lithium-based batteries to refining pharmaceutical synthesis, the Li molar mass—approximately 6.94 g/mol—serves as a pivotal benchmark.
Its significance extends beyond a mere number on the periodic table: it bridges theory and practice in ways that shape modern science and technology. Understanding Li’s molar mass begins with the fundamental definition: it represents the mass of one mole of lithium atoms, equal to 6.94 grams per mole. This value arises from Li’s atomic weight, defined at 6.94 atomic mass units (amu), normalized to the International System of Units (SI).
The precision of this measurement—rooted in mass spectrometry and modern analytical techniques—ensures consistency across laboratories worldwide.
Bridging Atomic Identity and Mass: Why Li Stands Out Lithium’s relatively low molar mass, second only to lithium’s position among the lightest alkali metals, contributes to its unique behavior in chemical systems. With an atomic number of 3 and only three protons, Li packs a surprisingly compact mass into a small atomic structure.
This low molecular density influences its electrochemical properties—especially relevant in energy storage technologies. The molar mass of lithium directly impacts volume and density calculations critical for battery design. For instance, lithium-ion batteries rely on Li’s favorable ratio of mass to charge capacity, enabling lightweight, high-energy storage solutions that power smartphones, electric vehicles, and renewable grids.
As energy demands grow, so does the strategic value of understanding these atomic-level perimeters.
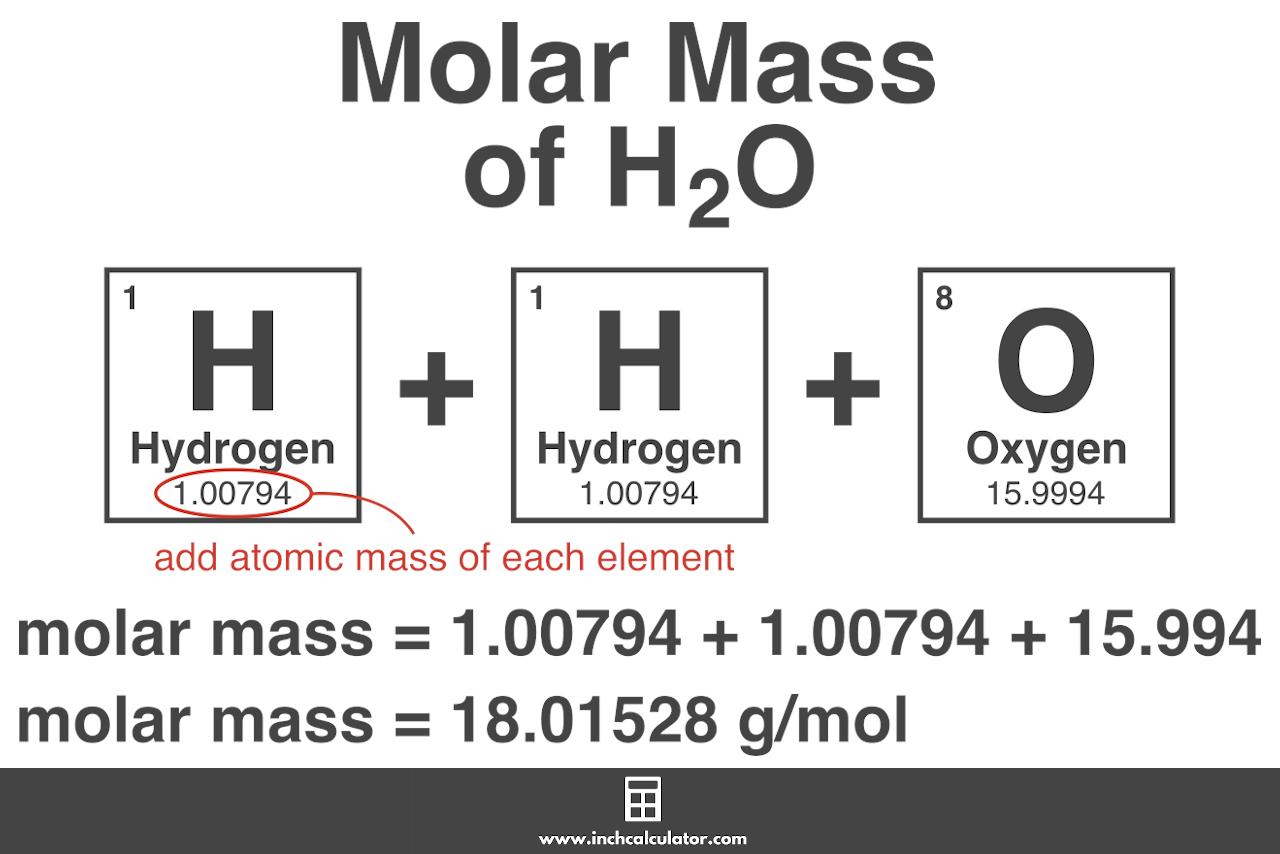
Calculating Li’s Molar Mass: From Equation to Real-World Impact Li’s molar mass is derived from its atomic weight of 6.941 metallic units and Avogadro’s constant (6.022×10²³ atoms/mol), yielding: Molar mass = 6.941 atoms/mol × 1.66054×10⁻²⁷ kg/atom ≈ 6.944 g/mol — consistent with the accepted value of 6.94 g/mol. This exactness ensures reliable molar ratios in chemical equations.
Consider a reaction involving lithium: 2Li + CuSO₄ → Cu + Li₂SO₄. The molar mass enables chemists to convert grams to moles with precision, enabling stoichiometric predictions critical for yield optimization and waste reduction in industrial synthesis.
Applications of Li Molar Mass Beyond the Bench
- **Pharmaceuticals and Drug Development** In medicinal chemistry, Li’s molar mass aids in modeling lithium-containing drug molecules or trace elemental carriers.Even minute lithium doses require accurate mass calculations to maintain therapeutic safety and efficacy. The molar mass supports pharmacokinetic modeling, ensuring proper dosing and minimizing toxicity risks. - **Materials Science and Nanotechnology** Lithium’s role in advanced materials—such as lightweight alloys, solid electrolytes, and cachet-layer thin films—depends on precise atomic mass data.
Understanding Li’s molar mass allows researchers to engineer structures with tailored electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. - **Environmental Chemistry and Geochemistry** Lithium footprints appear in natural systems, from geothermal brines to sediment layers. Accurate molar mass values enable environmental scientists to track lithium dispersion, assess mining impacts, and model natural geochemical cycles influencing water and soil chemistry.
Li Molar Mass: A Cornerstone of Modern Science
Li’s molar mass—though infinitesimally small compared to heavier elements—eserts outsized influence across chemistry’s evolving landscape. It underpins stoichiometry, drives innovation in energy and material sciences, and supports precision in pharmaceutical and environmental research. As global scientific and industrial ambitions expand, the relentless focus on atomic-scale accuracy becomes increasingly vital.Li’s molar mass, a constant yet dynamic figure, exemplifies how fundamental measurements catalyze transformative advancements. In laboratories and engineering fields alike, this number stands not as mere data, but as a silent architect of discovery—proving that even the lightest elements shape the heaviest impacts.


Related Post

John Huck Fox 5 Vegas Empowers Players with Real-Time Vegas Tips via New Digital Hub

Did Amal Clooney Use a Surrogate? Unraveling the Truth Behind Her Motherhood Journey

Debunking The Myth: Did The Pioneer Woman Succumb To Cancer? Unraveling The Truth

Zipstring’s Shark Tank Moment: What Followed the Surprising Updates on the Fifth-Generation Smart Shark

