NASA’s Budget Surge: What’s Driving America’s Space Exploration Funding in 2024
NASA’s Budget Surge: What’s Driving America’s Space Exploration Funding in 2024
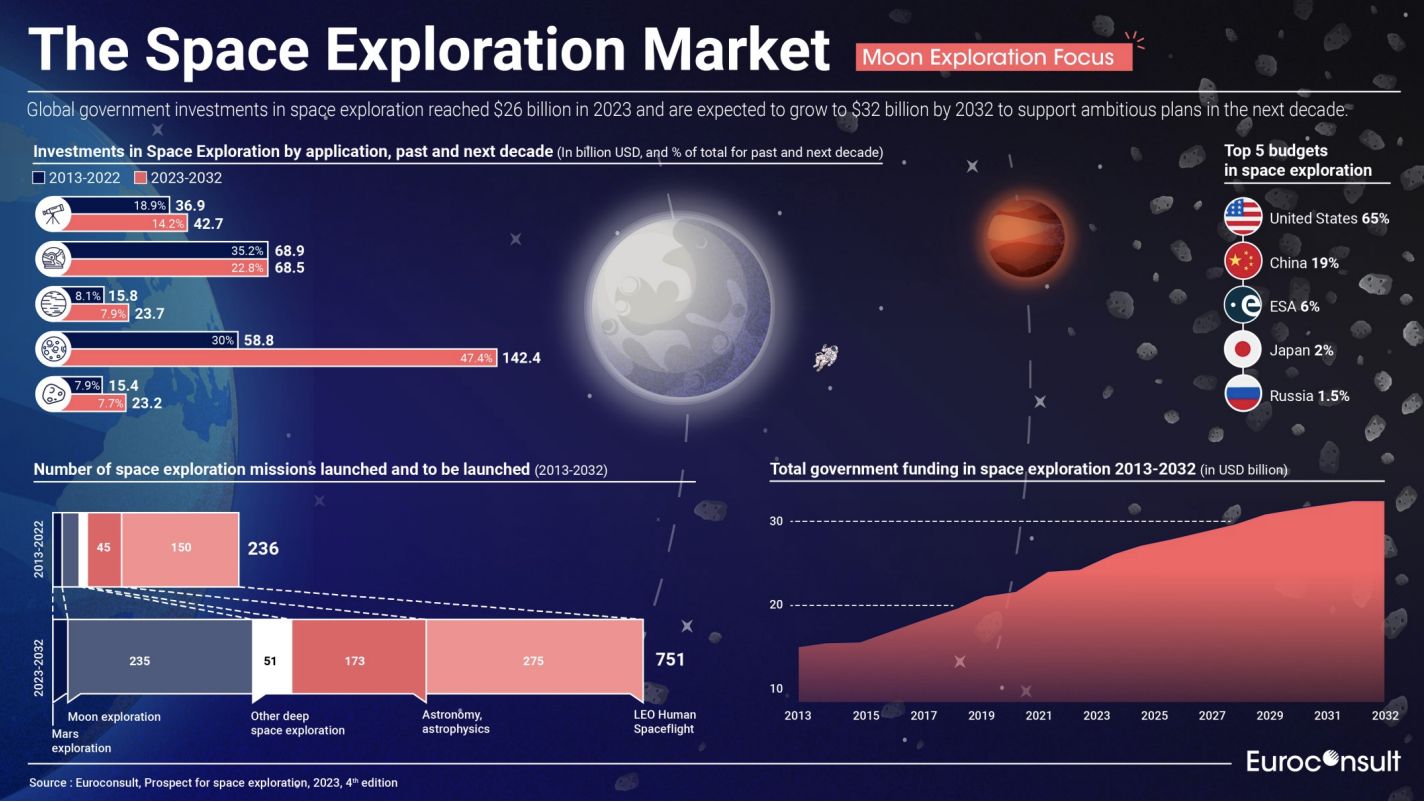
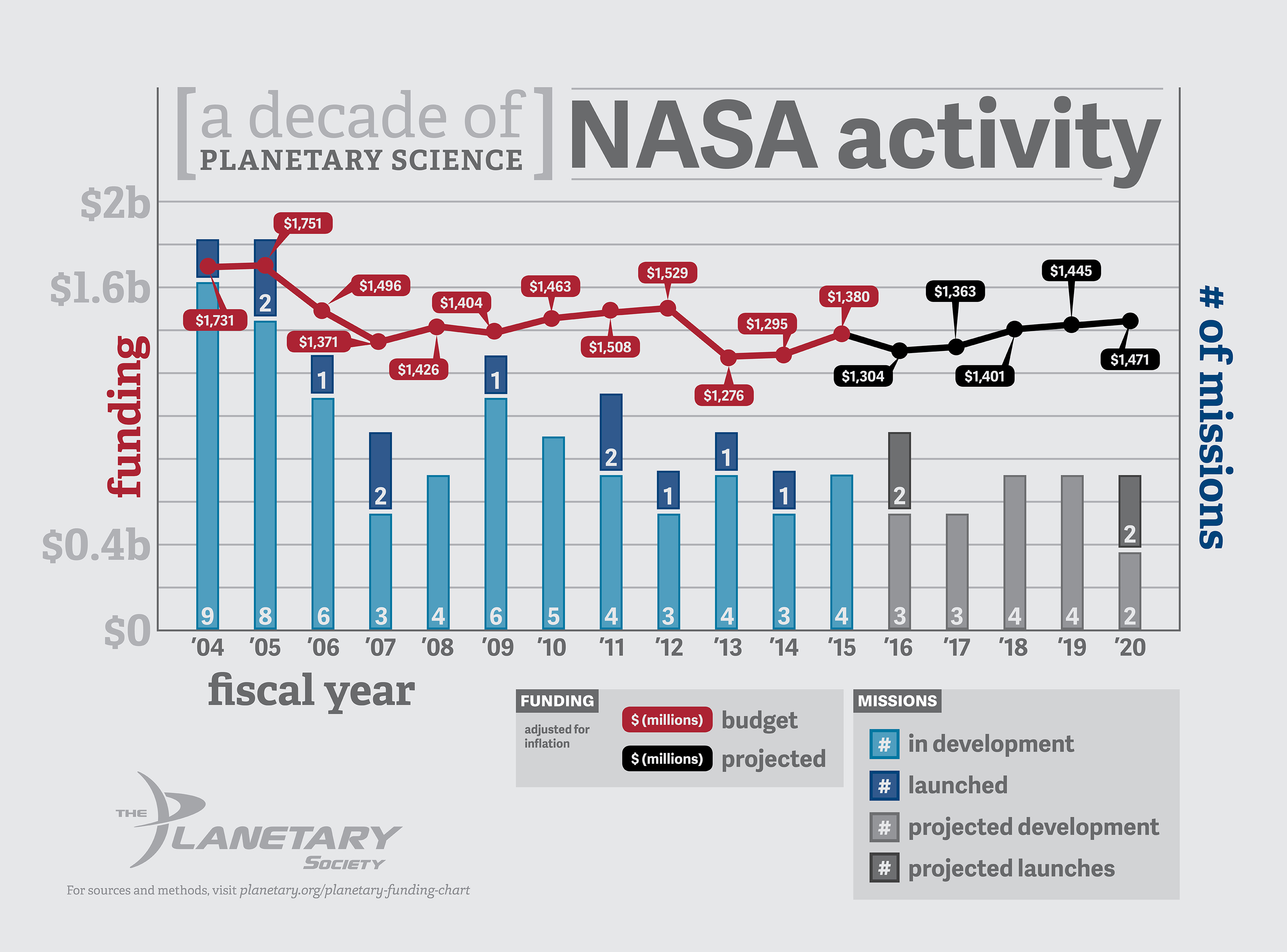
NASA’s fiscal 2024 funding announcement marks a transformative chapter in U.S. space exploration, with a record budget that signals renewed confidence in humanity’s quest beyond Earth. After years of steady investment, the agency has secured $27.2 billion—an increase of 6% over the previous year and the highest level in over a decade.
This funding reflects not just a budget line item, but a strategic commitment to accelerating deep-space missions, strengthening international partnerships, and fostering private-sector innovation. NASA Administrator Bill Nelson described the move as “a bold investment in the future—both for our nation and for all who wonder what lies beyond our atmosphere.”
At the heart of this year’s budget shift is a focus on sustaining momentum toward Mars and returning humans to the Moon. The Artemis program, NASA’s flagship effort to establish a lasting lunar presence, now stands at the center of funding allocations.
This year, NASA has allocated $5.9 billion for Artemis, up from $4.7 billion in 2023, enabling critical work on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, Orion spacecraft modifications, and the Human Landing System. “With this increase, we’re not just building rockets—we’re building pathways,” said NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy. “The Moon is our proving ground; Mars is our long-term horizon, and we’re funding both.”
One of the most impactful budget changes supports commercial partnerships, a cornerstone of NASA’s evolving strategy.
The agency committed $4.3 billion to private industry—up 12% from last year—to accelerate development of lunar landers, spaceflight infrastructure, and science missions. Contracts awarded to companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Astra underscore a shift from direct procurement to collaborative innovation. “Commercial partnerships reduce risk, lower costs, and unlock breakthroughs faster,” explained senior NASA budget analyst Dr.
Linda Thompson. “We’re not doing it alone—and the market is proving itself an invaluable partner.”
Key recipients include SpaceX for its Starship HLS variant, Blue Origin for advanced lunar mobility systems, and Rocket Lab for small-satellite launch capabilities. These investments aim to create a sustainable lunar economy while building closed-loop capabilities for deep-space operations.
Technological development continues to dominate mid-budget priorities, with NASA directing $3.2 billion to cutting-edge research in propulsion, robotics, and in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). Advanced green propellants, next-gen ion thrusters, and AI-driven autonomous systems for planetary rovers are among the projects gaining traction. The agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, which oversees these efforts, notes that “every dollar here is an investment in systems that will protect future crews and extend mission reach.” Recent testing of MOXIE-inspired oxygen production systems on Mars analog sites exemplifies progress toward using local materials to reduce reliance on Earth resupply.
Scientific exploration remains a high-priority beneficiary, with $3.1 billion allocated to astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics, and planetary research.
The James Webb Telescope’s extended mission, Europa Clipper’s flyby preparations, and the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s development all depend on sustained funding. “We’re not just observing the universe—we’re decoding its secrets,” stated Dr. Nicola Fox, Associate Director for Science.
“The science budget enables missions that will redefine our understanding of planets, stars, and the conditions for life.”
The updated budget also emphasizes Earth and space domain awareness, with $1.9 billion dedicated to monitoring climate change, asteroid threats, and space weather. Enhanced satellite constellations and ground-based tracking systems are being deployed to detect near-Earth objects earlier and improve global environmental data accuracy. This dual focus strengthens planetary defense and supports national security interests.
As NASA’s former Chief Scientist Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen noted, “Earth and space are inseparable. Better observation today ensures safer, more resilient systems tomorrow.”
Behind the numbers lies a transformed NASA workforce and supply chain, with funding supporting over 300,000 jobs across 49 states.
Small and medium enterprises alike are benefiting from streamlined procurement and innovation grants, reinforcing a diverse and agile space economy. From lunar landers to Mars-bound rovers, the 2024 funding reflects a calculated, forward-looking investment. It acknowledges that space exploration is no longer a distant dream but a present-day imperative—one funded with urgency, precision, and purpose.
As NASA prepares to send humans deeper into space than ever before, the budget is not just a financial statement; it’s a blueprint for the future of human discovery.
In a rapidly evolving global space landscape, this budget surge solidifies the United States’ leadership role. By coupling bold ambition with deliberate investment, NASA is building not just spacecraft—but a legacy.
Every mission funded today fuels the next generation of explorers, scientists, and innovators equipped to answer the most profound question: what comes next beyond Earth?

Related Post

Navy Federal FDIC Insured: Your Ultimate Shield for Savings and Security

The Ugly Sonic Rebellion: How a Distorted Classic Redefined Gaming Identity

Kendall Jenner’s Sex Life Under Scrutiny: Power, Fame, and the Public’s Insatiable Curiosity

Unrivaled Talent: The Story of CJ Wallace, Notorious B.I.G.’s Dual Legacy Through Yanna and Wallae

