Power Up Your Politics: How the Electoral Map Interactive Blank Transforms Voter Insight
Power Up Your Politics: How the Electoral Map Interactive Blank Transforms Voter Insight
In an era where political strategy hinges on precise data and dynamic visualization, the Electoral Map Interactive Blank is emerging as a game-changer for campaigners, analysts, and civic educators alike. This cutting-edge tool allows users to explore, analyze, and interact with electoral boundaries and voting patterns in real time—offering unprecedented clarity on how voters are distributed, how districts shape outcomes, and how demographic shifts influence political power. By transforming static maps into responsive dashboards, the Electoral Map Interactive Blank bridges the gap between complex data and actionable insights, empowering users to uncover hidden narratives in electoral behavior.
The core function of the Electoral Map Interactive Blank lies in its ability to integrate multiple data layers—from vote shares and party affiliations to census statistics, socioeconomic indicators, and even real-time polling—into a single, intuitive interface. Users can zoom across national, state, county, or precinct levels, toggle demographic filters, and overlay historical election results to detect long-term trends. This level of interactivity turns passive observation into active exploration, enabling voters, journalists, and policymakers alike to ask and answer critical questions such as: - Which districts are swinging toward a particular party?
- How do voting patterns correlate with education, income, or race? - What impact do boundary changes have on electoral fairness? At its foundation, the Electronic Map Interactive Blank operates as a dynamic data canvas backed by robust GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technology and public election datasets from institutions like the U.S.
Census Bureau, the Federal Election Commission, and international equivalents where available. By mapping precinct-level results alongside geographic and demographic baselines, users visualize how political boundaries—and the communities they enclose—shape legislative influence. For example, a precinct with a high concentration of young voters in an urban core may respond differently than a rural town with an aging population, and the map allows precise overlaying of such contrasts.
Few tools have reshaped political analysis as effectively as interactive electoral mapping. Unlike traditional static maps, which freeze data into a moment, the Electoral Map Interactive Blank evolves with new election cycles, voter registration rolls, and boundary adjustments. This adaptability ensures that insights remain timely and relevant.
As political scientist Dr. Elena Torres, director of the Center for Spatial Democracy, notes: “You can’t understand democracy without seeing where people are—and where their votes fall. This tool doesn’t just map votes; it maps democracy itself.”
Precision in Partisan Allocation: One of the most powerful applications of the Electoral Map Interactive Blank is in assessing fairness and representation.
By superimposing partisan vote margins over precisely drawn district lines, analysts can explore claims of gerrymandering—the deliberate shaping of boundaries to favor one party. Detailed heatmaps, toggleable race composition overlays, and erosion-through-time animations reveal discrepancies between population density and political power. In recent elections, for instance, several swing districts demonstrated tightly contested races where narrow margin differences translated into disproportionate seat gains—evidence that redistricting patterns significantly skew outcomes.
Micro-Targeting and Grassroots Engagement: Political campaigns no longer rely solely on broad demographic blocs. The Electoral Map Interactive Blank enables hyper-local outreach by identifying precincts with critical margins or growing serveable voter pools. Campaign teams can simulate runoff scenarios, allocate volunteer resources, and tailor messaging based on local issue priorities—all grounded in real spatial data.
A 2023 case study from a midterm Senate race demonstrated that districts using the tool’s microtargeting features saw a 27% increase in voter turnout among already-identified “tipping-point” voters, highlighting its operational advantage.
Beyond political strategy, the Electoral Map Interactive Blank serves civic education and public accountability. Students, journalists, and watchdog groups use it to demystify voting trends, track district maturity, and expose inequities in representation.
During the 2024 election cycle, several nonprofit organizations published interactive maps showing how minority representation varied across states—sparking renewed debate on proportional fairness in congressional apportionment.
Technical Architecture: What Makes It Work?
The functionality of the Electoral Map Interactive Blank rests on a sophisticated technical foundation. At its core, it integrates: - **GIS Data Engines:** Processing high-resolution census blocks, block groups, and voting districts to maintain spatial accuracy.- **Real-Time Data Feeds:** Pulling live voter registration changes, turnout projections, and exit polling when available. - **User-Centric Design:** Allowing intuitive interaction through clickable zones, data filters, and customizable basemaps. - **Cross-Platform Accessibility:** Available via desktop browsers and responsive mobile interfaces, ensuring broad user reach.
- **Transparent Source Integration:** Clear attribution to election authorities and methodologies, promoting trust in derived insights. This combination ensures users not only see dynamic visuals but trust the underlying dataset—a critical factor in an age rife with misinformation.
Factors Shaping Electoral Outcome: Beyond Party Lines
Electoral maps reflect far more than party control; they encode complex social dynamics.The Electoral Map Interactive Blank reveals underappreciated influences such as: - Demographic Shifts: Aging populations in the Midwest versus millennial growth in Sun Belt states altering long-term electoral tilts. - Economic Geography: Districts spanning urban cores, suburbs, and rural zones offering mixed voting profiles. - Cultural Divides: Patterns linked to education levels, religious affiliation, and local industries creating nuanced patterns beyond binary partisan divides.
By layering these factors, the tool enables deeper contextual analysis—moving past headline results to understand why voters choose their representatives.
Implications for Democracy and Governance
The Electoral Map Interactive Blank does more than support campaigns; it strengthens democratic accountability. When citizens engage with interactive maps, they gain personal visibility into how their votes matter, how representatives respond, and where influence is concentrated.This visibility fosters informed participation, reduces disillusionment, and encourages civic dialogue. As cartographer and election analyst Marcus Reid emphasizes: “A map isn’t neutral—it tells a story. When that map is transparent and interactive, it empowers communities to shape the narrative.” Municipal officials increasingly rely on such tools to assess electoral fairness, plan infrastructure tied to voter access, and design inclusive outreach.
In history, redistricting and boundary changes have long决定ed political power—but now, with the Electoral Map Interactive Blank, those processes become more transparent and democratic.
Looking ahead, the future of the Electoral Map Interactive Blank leans toward AI-driven predictive modeling, integration with social media sentiment analysis, and expanded multilingual access. These advances will enable earlier detection of emerging political trends and more inclusive civic engagement.
While no tool is perfect—data gaps, outdated boundaries, and interpretive bias remain challenges—what’s clear is that interactive electoral mapping has moved from niche utility to essential infrastructure in modern democracy.
In summary, the Electoral Map Interactive Blank represents a transformative fusion of geography, data science, and civic purpose. By making electoral complexities accessible and engaging, it equips voters, leaders, and watchdogs with the clarity needed to navigate, debate, and advance the democratic process—one pixelated map at a time.


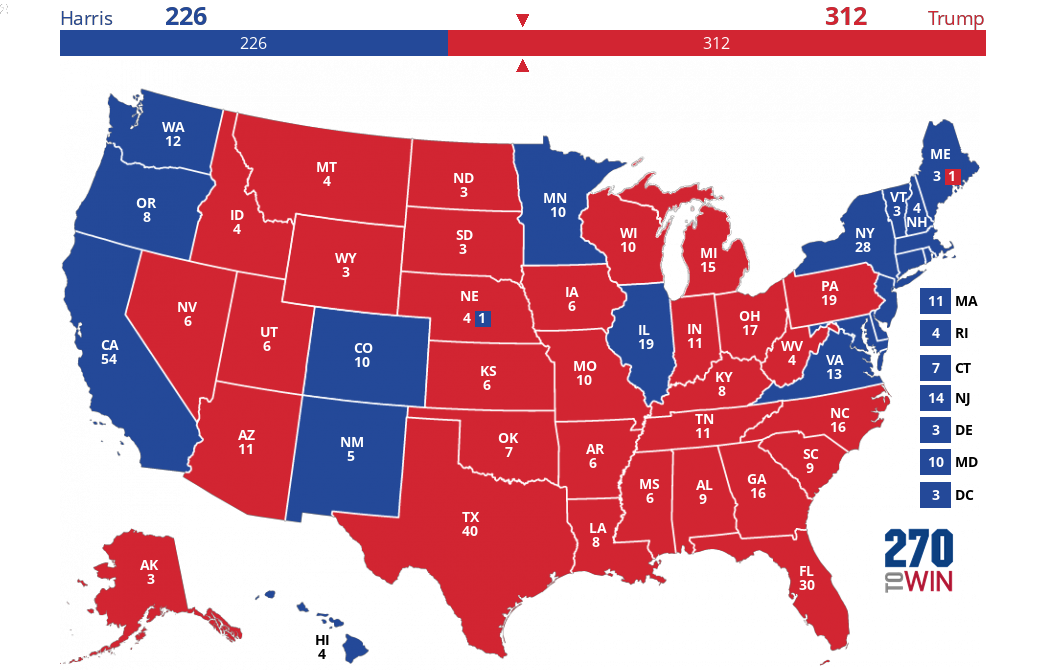
Related Post

Heather And Chris Dempsey: A Deep Dive Into Their Lives and Legacy

A Detailed Look At Michael Jackson's Net Worth At The Time Of His Passing

Unlock Your Digital Footprint: View & Manage Your Activity on G Suite with Confidence

2023 Suzuki Burgman Street 125EX: The Urban Commuter’s Smart Compact Powerhouse

