Real Id Requirements Pa: The Essential Blueprint for Legitٍ Endorsements in a Fraud-Resistant Era
Real Id Requirements Pa: The Essential Blueprint for Legitٍ Endorsements in a Fraud-Resistant Era
In an environment where digital impersonation and document fraud are escalating, governments and regulatory bodies are tightening validation standards to ensure trust in official identification. Real Id Requirements Pa—officially known as Real Identity Assurance (RIA) frameworks—represent a comprehensive set of guidelines and protocols designed to guarantee that versions of identification documents, such as driver’s licenses and state IDs, carry tamper-proof credentials verified through secure, standardized processes. These requirements are not merely procedural hurdles but foundational safeguards that protect identities, reduce fraud, and strengthen public confidence in government systems.
As digital services increasingly demand reliance on physical IDs, understanding the real id standards is crucial for individuals, businesses, and institutions aiming to comply with evolving legal expectations while maintaining operational integrity.
Real Id Requirements Pa encompass a multi-layered framework rooted in authenticity, security, and interoperability.
At their core, these standards mandate strict verification of both the physical and digital attributes of state-issued IDs, ensuring each credential can be verified against government databases in real time. This is achieved through advanced technologies including photo ID, continuous data validation, and encryption protocols that prevent forgery and alteration.
Key components of Real Id Requirements Pa include: - **Biometric Integration:** Most modern real IDs now embed biometric data—such as fingerprints or facial recognition templates—directly into the card or digital format, creating a unique, verifiable identifier that links individual identity with government records.
- **Tamper-Evident Security Features:** From micro-printing and holographic overlays to UV-reactive inks and embedded chips, these physical protections make unauthorized copying or substitution exceedingly difficult.
- **Centralized Authentication Systems:** State and federal entities collaborate via secure databases that cross-check ID data with national registries, ensuring consistency and real-time validation across jurisdictions.
- **Standardized Quality Assurance:** Each state must adhere to federally mandated performance levels measured through rigorous testing, ensuring all issued IDs meet the same high bar for reliability and security.
These requirements emerged in response to growing threats posed by document fraud, identity theft, and cyber-enabled impersonation. Historically, inconsistent state-level ID standards allowed for vulnerabilities that fraudsters exploited to forge credentials across borders.
The Real Id Rules, established and refined by the Department of Homeland Security’s Office of Identity Management and adopted incrementally by states since 2016, represent a national effort to harmonize protection mechanisms and elevate trust in public documents.
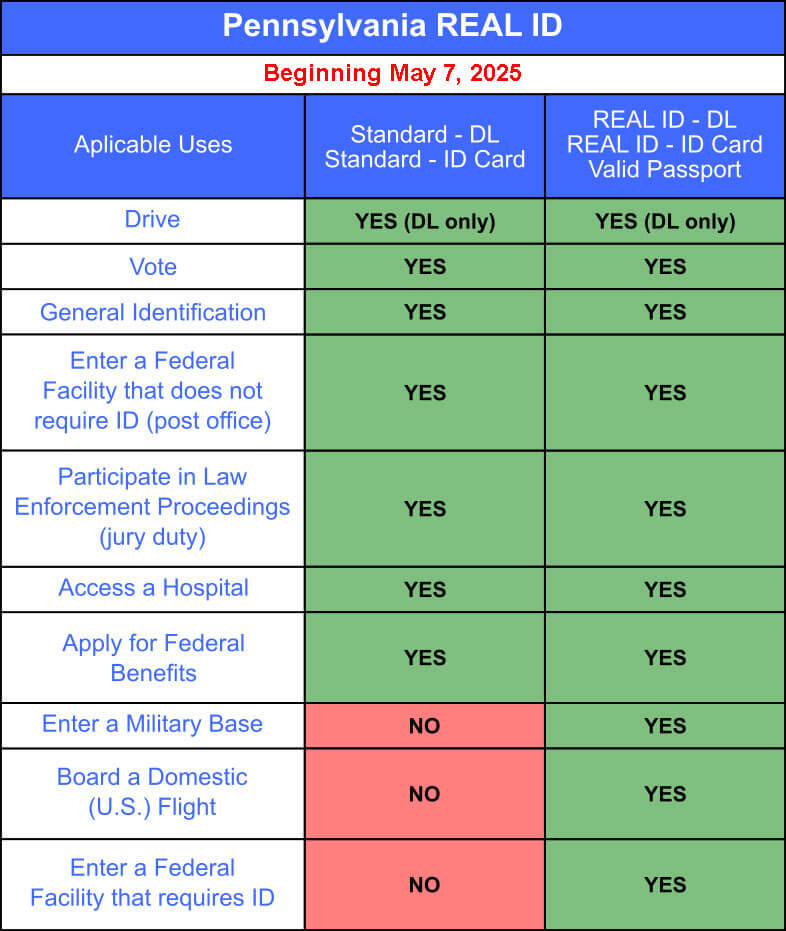
For example, under the Real Id framework, a driver’s license must include both a photo ID and a unique serial number linked to a national database. This allows law enforcement and integrated services—including background checks, driver screenings, and access controls—to instantly confirm the ID’s legitimacy, reducing false or stolen documents from slip through the cracks.
Companies relying on government-issued ID verification—such as financial institutions, employers, and lenders—must now comply with these stringent standards. Failure to validate IDs through RIA-approved methods risks legal penalties, financial exposure, and reputational harm.
As one compliance officer from a major payroll services firm noted, “Authentication is no longer an afterthought. It’s the backbone of trust—every verification step must align with Real Id Rules to avoid liability and ensure data integrity.”
The implementation of Real Id Requirements Pa varies by state due to differing timelines and resource capacities, but core principles remain consistent. States must conduct regular audits, update verification software, train personnel on new protocols, and publicly disclose compliance status to maintain transparency.
Critics argue the burden of compliance may strain smaller jurisdictions or businesses, especially during system upgrades.
However, proponents emphasize long-term benefits: reduced fraud losses, streamlined services, and heightened public confidence—factors that ultimately support safer, more resilient communities.
Looking ahead, Real Id Requirement Pa frameworks are evolving to incorporate emerging technologies. Research into dynamic credentials, blockchain-based identity records, and AI-driven verification promises to further reduce vulnerabilities while improving user experience. The vision is clear: a future where identity is not just verified, but responsibly managed, encrypted, and trusted at every interaction point.
Whether navigating workplace onboarding, financial due diligence, or public services access, Real Id Requirements Pa now define the new baseline for identity assurance—ensuring that every ID presented is not only genuine, but legally and technically certified to serve its purpose in an interconnected world.
Technical Foundations: What Ensures ID Authenticity
The backbone of Real Id Requirements Pa rests on three interlocking pillars: verification accuracy, security engineering, and system interoperability. Each element serves as a sentinel against fraud, ensuring that every ID is more than a physical token—it is a digital assurance product.
Verification Accuracy is achieved through real-time database matching. When an ID is presented, whether in person or digitally, its data—photo, name, date of birth, ID number—is immediately cross-referenced with national and state-level identity repositories.
This instant check compares against known issuances, flagging mismatches or red flags such as duplicate numbers or expired records. “Accuracy isn’t optional—it’s the frontline defense,” stated a senior compliance analyst from the National Identity Task Force. “Even a minor error can compromise an entire validation chain.”
Security Engineering embeds layers of protection directly into the ID format.
Modern real IDs use encrypted microchips storing biometric templates, making tampering nearly impossible without specialized tools. Physical features like holograms and ultrasonic printing add visual deterrents, while tamper-evident seals degrade visibly upon unauthorized handling. The goal is a multi-sensory verification experience—visual, digital, and forensic—that leaves no room for substitution.
System Interoperability


Related Post

9am Ist To Est

All You Need to Know About Khalyla Kuhn’s Relationship with Bobby Lee: The Boyfriend Behind the Headlines

How Old Is Maria Bartiromo’s Husband? Decoding the Age of a Celebrity Marriage

He Is Risen: The Resurrection That Shakes Faith and History

