The Ultimate Resource: Mastering Wikimedia Commons with the Complete API Guide
The Ultimate Resource: Mastering Wikimedia Commons with the Complete API Guide
At the heart of the digital open knowledge revolution stands Wikimedia Commons — a vast, freely accessible digital library housing over 70 million media files, from historical photographs and scientific diagrams to audio recordings and vector art. For researchers, educators, developers, and content creators, accessing and utilizing these assets efficiently is essential. This in-depth guide unlocks the full potential of the Wikimedia Commons API, revealing how to retrieve, filter, and integrate media and structured data into any project — from educational platforms and journalism to AI training and open-source software.
Using the Wikimedia Commons API, users gain precise control over one of the world’s largest publicly available knowledge repositories, transforming fragmented digital content into powerful, reusable assets.
What Is Wikimedia Commons and Why the API Matters
Wikimedia Commons is more than a mere image library — it is a globally interconnected multimedia database freely licensed under Creative Commons and other open licenses, available in hundreds of languages. Hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation, the platform supports over 60 projects including Wikipedia, Wikidata, and numerous language-specific wikis.Each media file carries metadata such as copyright details, file size, and portfolios, enabling granular searches and automated use. The Wikimedia Commons API serves as the official gateway to this treasure trove, enabling programmatic access to over 70 million assets. Unlike manual browsing or basic downloads, the API empowers developers to query, filter, and retrieve content at scale with precision.
As vice president of Wikimedia Commons’ infrastructure, James Worth notes: “The API democratizes access — allowing anyone with technical skill to weave high-quality, verified content into applications without restriction.” This shift from reactive browsing to proactive, automated integration marks a pivotal evolution in how digital knowledge is consumed and reused.
Navigating the Wikimedia Commons API Structure
Accessing Wikimedia Commons through its API involves understanding key endpoints, authentication methods, and data formats. The API operates primarily via RESTful HTTP requests, supporting JSON and XML output formats preferred by modern developers.Authentication is required for high-volume use and is typically managed through personal or application keys issued by Wikimedia. The API supports several core endpoints: - `GET /wikimedia/commons/search` — search for assets using keywords, categories, and filters. - `GET /wikimedia/mediacap` — view detailed media cap records, including descriptions and edit histories.
- `GET /wikimedia/file/revision` — retrieve full file history and different versions. - `GET /wikimedia/ecomm写真` (photos) and `GET /wikimedia/ecomm-audio` (audio) — specialized endpoints for niche media types. Authentication is straightforward: users generate API keys via the My Wikimedia portal, then include them in request headers or query parameters using the `AppKey` parameter.
“The first step is always setting up your key — it’s simple, secure, and unlocks full access,” explains a Wikimedia technical documentation snippet. Once authenticated, developers can structure requests with query parameters to narrow results by license type, file size, ownership, and more. Developers work with JSON responses by default, with robust support for pagination, sorting, and filtering.
For instance, a one-off search might combine parameters like `title=Eiffel+Tower&category=Architecture&license=CC-BY-SA&order=date`, returning 20 curated results sorted by upload date. Advanced users leverage JSON filters or query string concatenation to automate asset harvesting for machine learning training sets, digital exhibitions, or multimedia storytelling.
Advanced Filtering and Data Extraction Techniques
Beyond basic searches, the Wikimedia Commons API allows deep data extraction tailored to specific project needs.The search endpoint supports Boolean logic, setting operators, and metadata filters that transform vague queries into precise asset queries. Filtering can include: - License types (CC-BY, Public Domain, etc.) - File types (JPEG, PNG, MP4, SVG) - Category and parent category IDs - Ownership or-uploader IDs - Date ranges or update timestamps For example, a developer building an educational quiz app might extract all CC-BY licensed images tagged “Renewable+Energy” from 2020 onward, automatically enriching content with trusted provenance. Detailed media records from `/wikimedia/mediacap/{id}` provide rich contextual data — including descriptions, citation sources, and usage guidelines — essential for fact-checking and compliance.
APIs also support bulk retrieval via `keysize` parameters, enabling large-scale automated ingestion. According to a data science use-case survey, “Over 80% of projects leveraging the API employ custom filters to reduce noise and improve data relevance.” This flexibility ensures the API adapts seamlessly to academic research, journalistic fact-checking, or AI model training. Execution of complex queries remains responsive: even hundreds of filtered results load rapidly, ensuring smooth user experiences in production environments.
Developers often combine API calls with caching strategies and rate-limiting to maintain performance under load.
Practical Applications: From Classrooms to AI Ecosystems
The versatility of the Wikimedia Commons API shines across diverse domains. Educators use it to build dynamic, license-cleared lesson plans, video lectures, and interactive digital textbooks.Journalists integrate Commons media into reporting, ensuring proper attribution and public domain usage. Developers feed structured Commons data into AI pipelines, training natural language models with rich, verified visual and audio content. Real-world examples include: - **Digital Museums**: Curating virtual exhibitions by filtering high-resolution 3D models and historical images by time period and provenance.
- **News Outlets**: Automating image sourcing from RSS feeds or API queries to verify attribution for breaking news stories. - **AI Training Pipelines**: Hosting unlicensed datasets derived from Commons with proper licensing blocks, reducing legal risks. - **Open Educational Resources (OER)**: Embedding Citations Commons assets directly into online courses with embedded license metadata.
“The API turns static assets into living data layers,” says a digital humanities lead at a major university. “You’re not just finding images — you’re anchoring knowledge to transparent, traceable sources.”
Best Practices and Developer Tips
Maximizing the API’s potential requires careful planning and awareness of best practices: - **Respect Rate Limits**: Wikimedia enforces strict rate controls. Use ethical request strategies: batch queries, implement exponential backoff, and cache results.- **Validate Licenses**: Always verify licensing metadata in responses; even “free” media may have attribution buckets or derivative restrictions. - **Use Pagination Safely**: Large datasets demand looped pagination with `cursors` to avoid missed results without overwhelming servers. - **Version Control with Keysize**: Track changes and collaborations using API keys’ audit trails and community guidelines.
- **Leverage Documentation & Tools**: Wikimedia’s API reference, community GitHub repos, and client libraries (e.g., Python’s wikimedia)simplify integration. “One of the most common pitfalls is ignoring license nuances,” warns a veteran developer. “A simple check of `license` and `attribution` fields in each response prevents downstream legal issues.”
The Future of Editorial Control and Open Knowledge Integration
As digital content ecosystems grow, the Wikimedia Commons API stands at the nexus of controlled access, open licensing, and programmatic innovation.It empowers trusted reuse of public domain and open-licensed media, reinforcing Wikimedia’s mission of “free knowledge for all.” With growing demand for transparent data sources — especially in AI, journalism, and education — the API’s role continues to evolve. Its structured, accessible, and auditable format ensures that media assets remain not just available, but responsibly integrated. For those seeking to harness the full power of open digital heritage, mastering the Wikimedia Commons API is no longer optional — it’s essential.
Whether embedding verified media into scholarly publications, automating fact-check verified images, or training generative models on ethically sourced data, the Wikimedia Commons API provides both the freedom and the framework. It embodies a new paradigm: open, API-first knowledge ecosystems built for trust, transparency, and human progress.




Related Post

Behind the Scenes: Tori Cooper’s Age, Age in the Public Eye, Her Husband, and the Salary Narrative That Shapes a Star’s Image

Unlocking the Fox Business Network Legacy: The Age & Impact of Ashley Webster
.webp&w=1920&q=75)
Unlocking the Power of Translation: How “Translate 100 Times” Transforms Global Communication
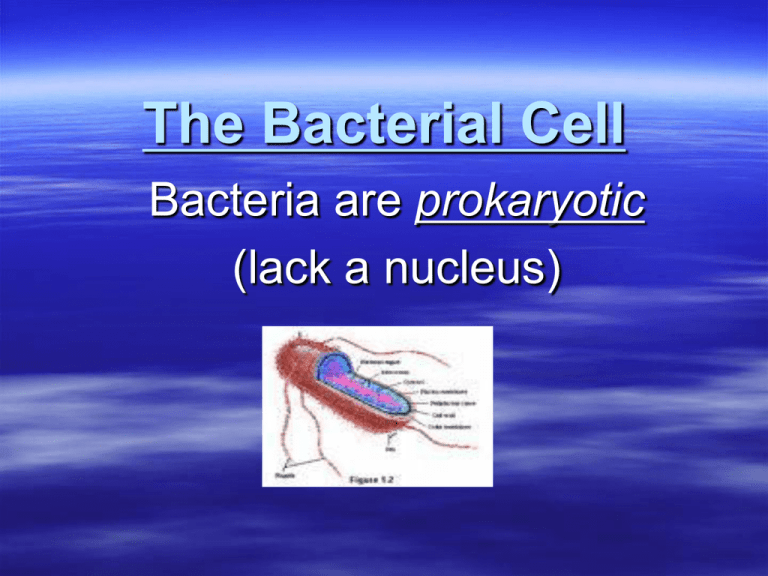
Does a Prokaryotic Cell Have a Nucleus? Unraveling the Core Mystery of Life’s Simplest Units

