Unlocking Global Financial Clarity: How Conversion Est Gmt Transforms Time-Zone–Driven Markets
Unlocking Global Financial Clarity: How Conversion Est Gmt Transforms Time-Zone–Driven Markets
In an era where multinational trade, real-time trading, and coordinated global communications define economic momentum, the Conversion Est Gmt—Conversion Established Greenwich Mean Time—has emerged as a pivotal standard in synchronizing financial data across disparate time zones. This critical timestamp marker, rooted in the universal reference of GMT, ensures that transactions, reports, and operational windows align precisely regardless of regional offsets. As global markets shrink and cross-border activity accelerates, the role of Conversion Est Gmt in eliminating confusion and enhancing accuracy has never been more decisive.
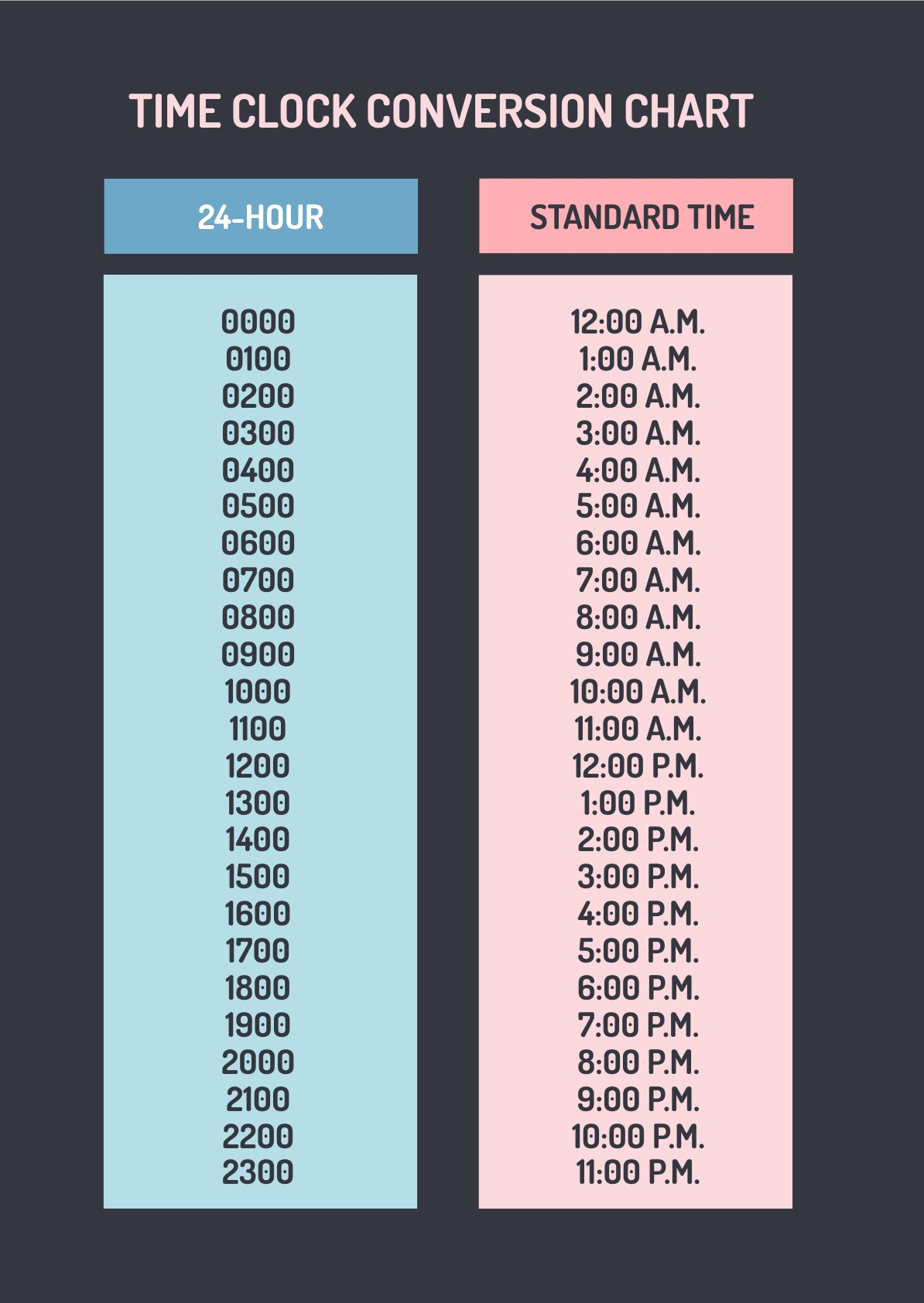
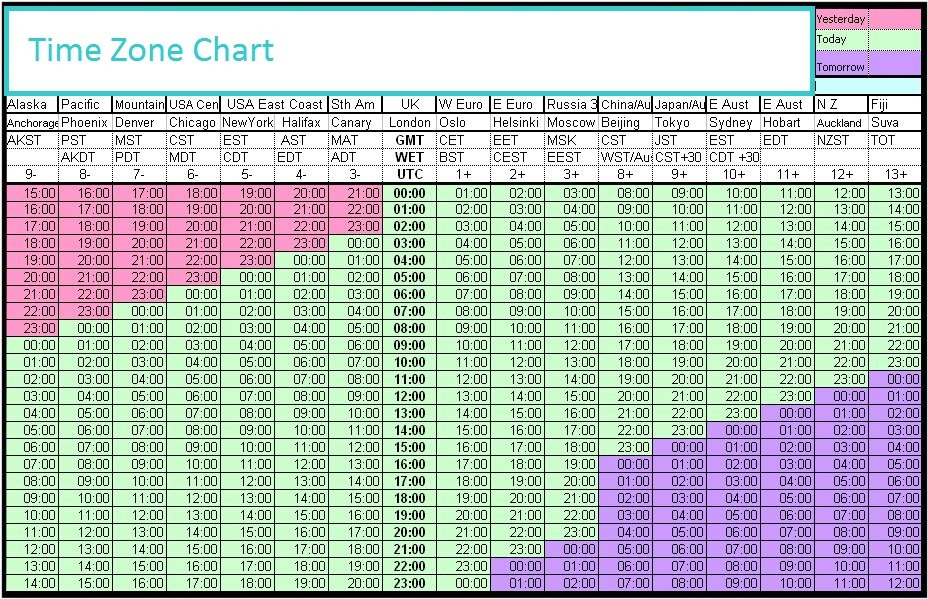
Conversion Est Gmt serves as the standardized temporal anchor that aligns financial data across all pressing global time zones. Unlike arbitrary local time conversions, it provides a uniform baseline, enabling seamless coordination in everything from brokerage settlements to multinational supply chain logistics. By anchoring all timestamps to a single, universally accepted reference—Greenwich Mean Time—this framework eliminates discrepancies that could distort reporting, delay transactions, or trigger compliance risks.
For firms managing operations across tolls of time, from New York and London to Singapore and Mumbai, Conversion Est Gmt delivers a single point of truth. The mechanism behind Conversion Est Gmt is deceptively simple yet profoundly impactful. It is not merely a time offset but a calibrated anchor point within the World Time Zone System, updating twice daily as GMT transitions alongside Greenwich’s astronomical meridian.
This precision ensures that every system, application, or human operator referencing Est Gmt accesses a synchronized reference. Whether tracking a stock trade initiated in Sydney that must reconcile with EPYC results filed in Frankfurt, or scheduling a live earnings call spanning ISDA agreements in London and operations in Tokyo, Conversion Est Gmt guarantees temporal integrity.
In practical terms, Conversion Est Gmt underpins critical systems across finance, logistics, and regulatory compliance.
Financial institutions rely on it to timestamp trades, reconciliations, and audit trails with millisecond accuracy, ensuring that discrepancies due to time misalignment are reduced to near zero. For example, algorithmic trading platforms use Est Gmt to synchronize buy/sell orders across global exchanges, preventing latency-driven arbitrage errors. Similarly, logistics firms depend on Conversion Est Gmt to coordinate shipments, warehouse hours, and customs clearances across jurisdictions where local time differences could otherwise cause miscommunication.
“Conversion Est Gmt isn’t just a technical detail—it’s the invisible scaffold that holds global operations together,” notes Dr. Elena Márquez, a global finance systems expert at the International Monetary Forum. “Without a unified time reference, even minor misalignments amplify into costly delays, failed judgments, or regulatory breaches.
This standard brings clarity in a chaotic world of overlapping markets.”
Beyond immediate operational use, Conversion Est Gmt plays a strategic role in regulatory reporting and audit readiness. Many jurisdictions mandate timestamp accuracy for tax filings, financial disclosures, and anti-money laundering checks. By anchoring all records to a consistent GMT baseline, organizations ensure compliance across borders, avoiding the frictions that arise from conflicting local time frames.
This standardization also supports real-time risk assessment, allowing compliance officers to monitor activities across time zones with confidence.
Implementation of Conversion Est Gmt, however, demands careful integration into existing IT architectures. Financial software, trading platforms, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems must recognize and correctly apply Est Gmt timestamps.
Legacy systems often struggle with dynamic time recalibration, making middleware or API-based transaction normalization essential. Best practices include: - Automating timestamp conversion using GMT-conformant libraries such as IANA’s time zone database. - Conducting regular validation checks to verify all logs reference Ex Gmt.
- Training personnel to interpret and report data using the standardized frame. - Maintaining audit trails that capture source time zone handling for compliance scrutiny.
The convergence of financial globalization and digital infrastructure has elevated Conversion Est Gmt from a niche time protocol to a universal operational imperative.
As markets grow more interconnected, the ability to operate across time without temporal friction becomes a competitive advantage. Institutions leveraging Est Gmt report reduced operational delays, fewer reconciliation errors, and stronger alignment with international reporting standards. For businesses, investors, and regulators alike, Conversion Est Gmt represents more than a timestamp mechanism—it is the foundation of synchronized global commerce.
In a world where a second gained in one region can cascade into minutes lost elsewhere, this precise synchronization ensures that no second, minute, or hour slips through the cracks. The widespread adoption of Conversion Est Gmt is not just a technical upgrade; it is a strategic necessity for any entity navigating the complexities of 21st-century time-driven markets.


Related Post

Who Is Emily Husband? Unraveling the Man Behind a Name That Echoes in English Naming Traditions

Behind the Curtain: Unveiling the Private Life of Jeffrey Dean Morgan and His Marvelously Enduring Marriage

A Boeing 707 Engine: The Pulse of Aviation’s Golden Era

All About Rory Farquharson: The Rising Star Shaping Modern Media and Creativity

