Unlocking Molecular Secrets: The Power of Benzoic Acid IR Spectrum Analysis
Unlocking Molecular Secrets: The Power of Benzoic Acid IR Spectrum Analysis
Benzoic acid’s infrared (IR) spectrum reveals critical insights into its molecular structure, functional groups, and purity—making it an indispensable tool in chemical research, forensic analysis, and industrial quality control. The distinctive absorption bands in the IR region serve as a molecular fingerprint, enabling scientists to verify identity, detect impurities, and understand chemical behavior with remarkable precision. For benzoic acid and related aromatic carboxylic acids, the IR spectrum provides a reliable, rapid, and non-destructive method to confirm structural integrity.
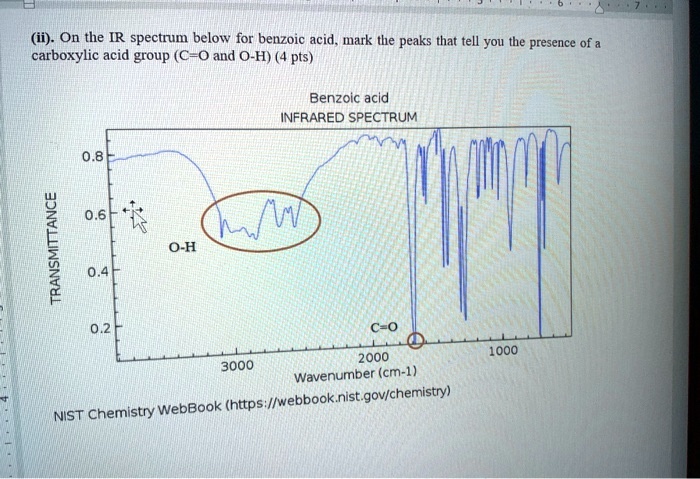
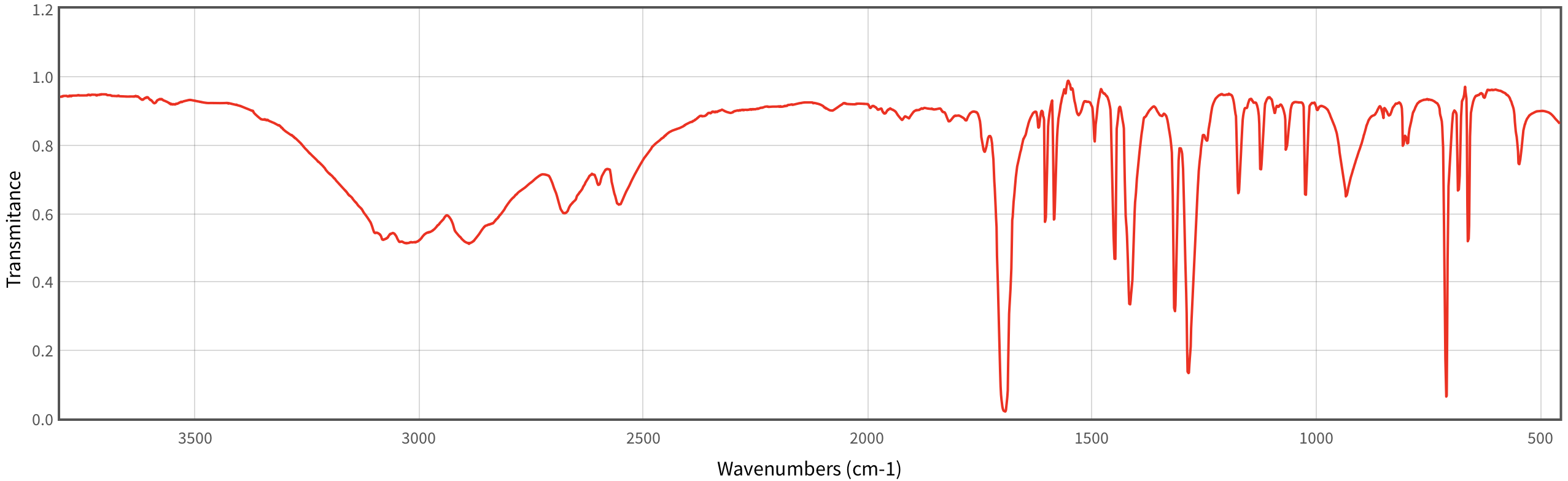
The primary diagnostic features of benzoic acid’s IR spectrum center around the characteristic absorption bands that correspond to key functional groups. The most prominent and diagnostic peak appears near 1700–1720 cm⁻¹, reflecting the strong carbonyl (C=O) stretching vibration of the benzoic acid – a hallmark of aromatic carboxylic acids. This peak is typically sharp and intense, distinguishing benzoic acid from unrelated compounds.
Equally important is the broad O–H stretching band centered at approximately 2500–3300 cm⁻¹, attributed to the acidic hydrogen of the –COOH group. Unlike aldehydes or ketones, benzoic acid exhibits a characteristic “B-bottom” bend vibration around 750–780 cm⁻¹, often visible only in high-resolution spectra, adding structural specificity. Beyond these primary markers, subtle shifts and additional absorptions offer deeper insight into molecular environment and intermolecular interactions.
For instance, hydrogen bonding between carboxylic acid molecules can broaden the O–H band, signaling dimer formation common in non-polar environments. The C–H伸缩 (immune region) vibrations between 3000–3100 cm⁻¹ provide clues about solvation and aggregation, while the C–O stretch near 1100–1200 cm⁻¹ confirms the presence of the aromatic ether linkage. Together, this spectral signature forms a comprehensive profile uniquely attributable to benzoic acid.
In forensic toxicology, IR spectroscopy serves as an immediate screening method to detect benzoic acid in biological samples, where it may appear as a degradation product or intentional compound. Industrial labs rely on IR analysis to monitor benzoic acid quality in pharmaceuticals, food additives, and antimicrobial coatings, where purity directly impacts efficacy and safety. The versatility and speed of IR spectroscopy make it more than a research tool—it is a cornerstone of modern analytical chemistry.
The Diagnostic Bands: Key IR Features of Benzoic Acid
The carbonyl stretch at 1700–1720 cm⁻¹ is the most definitive indicator of benzoic acid’s identity. This frequency typically falls in the symmetric stretch region of aromatic carboxylic acids, with minor vibrations extending higher due to conjugation with the benzene ring. The sharpness and consistent position of this peak distinguish benzoic acid from structurally similar derivatives like salicylic acid, which often shows a slightly shifted or broader carbonyl signal.The O–H stretching absorption between 2500–3300 cm⁻¹ is broad and intense, a clear sign of the carboxylic acid’s acidic proton. Its position and width are sensitive to hydrogen bonding; in crystalline or dilute solutions, the band may broaden significantly, reflecting intermolecular interactions. This feature is especially valuable in distinguishing benzoic acid from neutral aromatic carboxylic acids that lack acidic protons.
Additional vibrational modes contribute contextual information. The C–O stretch around 1200–1250 cm⁻¹ confirms the ether linkage, while the C–H in-plane bending (πـ vibration) near 720–735 cm⁻¹ offers evidence of aromatic ring planarity. These complementary bands collectively build a robust spectral profile, allowing confident identification even in complex mixtures.
Applications of Benzoic Acid IR Spectroscopy Across Industries
In pharmaceutical development, benzoic acid and its derivatives serve as key building blocks in drug synthesis and preservative formulations. IR spectroscopy plays a vital role in verifying intermediate compounds, ensuring that synthesized benzoic acid derivatives meet stringent purity and structural specifications. For instance, during the production of acethydrazide—a once-used antitubercular drug—IR analysis confirmed the presence and integrity of the benzoic acid moiety, preventing costly batch failures.The food and cosmetic industries leverage IR spectroscopy for quality assurance. In consumer products, trace amounts of benzoic acid act as effective antimicrobial agents, preventing spoilage. Fast-identifying IR scans enable rapid compliance checks, ensuring that products adhere to regulatory limits for preservatives.
This speed and precision reduce reliance on slower chromatographic methods, streamlining production oversight. Forensic laboratories apply benzoic acid IR analysis in toxicology screens to detect illicit use of benzoic acid as a covert additive or precursor in drug formulations. The non-destructive nature of IR allows forensic experts to analyze trace samples without extensive sample preparation, accelerating case resolution.
Plastic and polymer industries also benefit: benzoic acid is integrated into antimicrobial coatings, where IR spectra confirm its effective grafting to surfaces, validating antimicrobial claims. Environmental monitoring increasingly incorporates IR spectroscopy to track benzoic acid in water and soil samples, assessing its persistence and impact. The technique’s ability to detect low concentrations aids in understanding environmental fate, guiding remediation strategies and regulatory policies.
Advantages and Limitations of IR Spectroscopy in Benzoic Acid Analysis
IR spectroscopy offers compelling advantages for studying benzoic acid. It is rapid, requiring only minutes for analysis, with minimal sample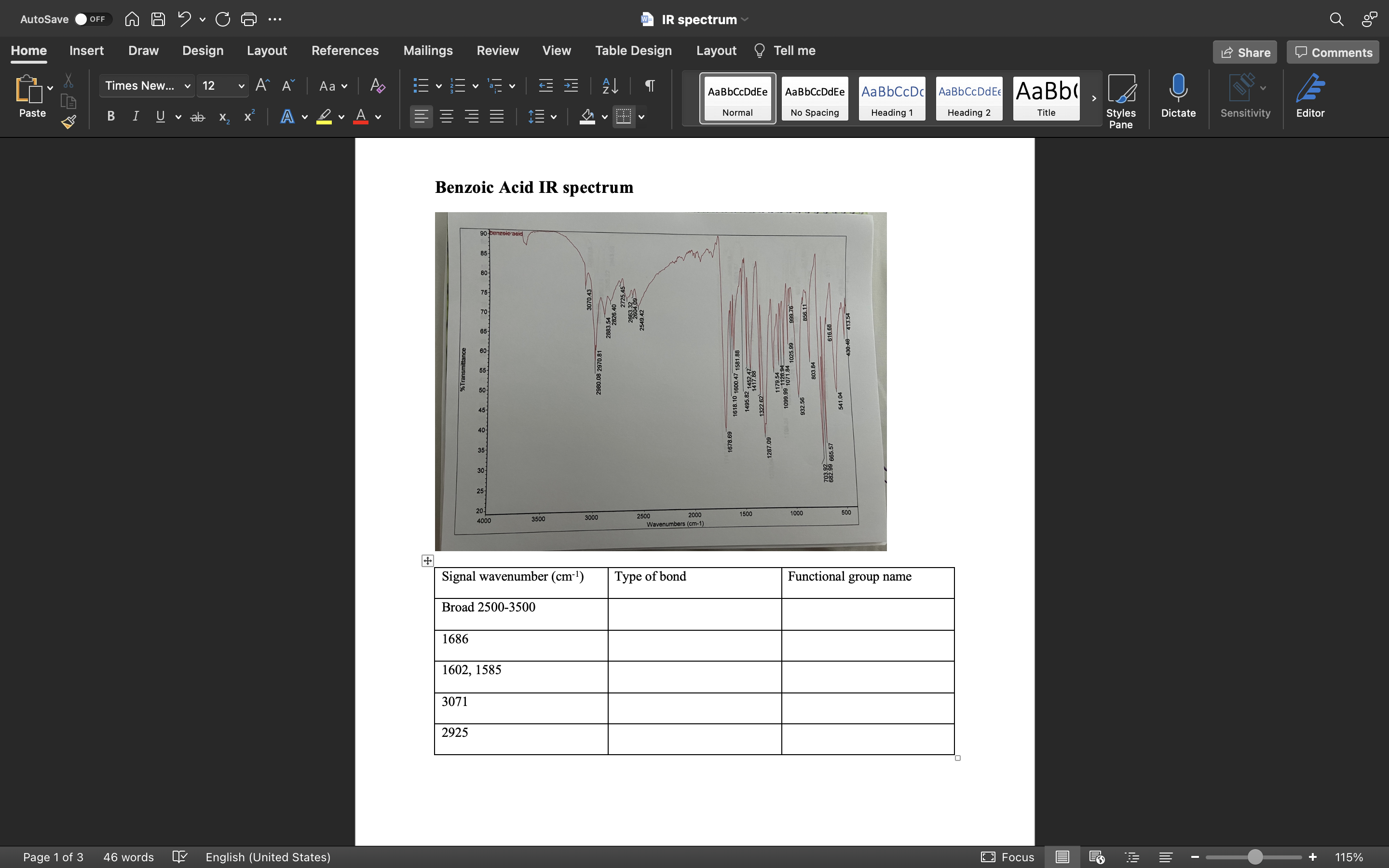
Related Post

Rshg2725mmRocketLauncher

Brandon T. Jackson’s Transformative Turn in Tropic Thunder: The Power of a Method Acting Marvel
Unpacking PoSci and MBTI: What CSe Reveals About Personality Typing — A Deep Dive

Ed Hurley Was More Than a Dresser: The Quiet Architect Behind Twin Peaks’s Soul

