What Does Agriculture Mean? The Lifeline of Civilization and Modern Innovation
What Does Agriculture Mean? The Lifeline of Civilization and Modern Innovation
Agriculture is far more than farming—it is the foundational human activity that sustains life, shapes economies, and defines cultures across continents and centuries. At its core, agriculture means the systematic cultivation of plants and rearing of animals to produce food, fiber, fuel, and other essential materials. It is the silent force behind human settlement, dietary stability, and industrial development, evolving continuously from ancient subsistence practices into a global, science-driven industry.
The word agriculture derives from Latin *ager* (field) and the suffix *-culture*, encapsulating the act of “working the land.” But its meaning extends beyond mere cultivation: it reflects a complex interplay of soil science, climate adaptation, genetic improvement, supply chains, and policy. As the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) asserts, “agriculture is the backbone of rural development and a critical pillar of global food security.” This dual role—practical sustenance and systemic integration—defines agriculture’s enduring significance.
From the earliest Neolithic settlements, agriculture enabled humanity to transition from nomadic hunter-gatherers to stable communities.
Domestication of wheat, rice, maize, and livestock allowed population growth, surplus production, and the rise of civilizations. Today, agriculture encompasses industrial-scale mechanization, precision farming technologies, and sustainable practices—all aimed at feeding a growing global population, projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050. Yet, agriculture remains deeply rooted in local ecosystems, adapting regionally to diverse climates, cultures, and resource availability.
Core Components: Cultivation, Livestock, and Ecosystem Stewardship
Modern agriculture integrates two primary domains: crop cultivation and animal husbandry, supported by ecological principles and technological innovation.Crop systems—ranging from staple grains like wheat and rice to specialty crops such as coffee and cocoa—depend on careful soil management, pest control, and breeding for resilience. Livestock operations involve breeding, feeding, and welfare considerations, providing meat, dairy, wool, and manure critical to farming systems.
Equally vital is agriculture’s expanding role in ecosystem stewardship.
Sustainable farming increasingly emphasizes soil health, water conservation, and biodiversity. “Regenerative agriculture is not just about growing food—it’s about healing the land,” notes Dr. Christine Jones, soil microbiologist and sustainability advocate.
Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and agroforestry help restore degraded soils, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and support pollinators, illustrating how agriculture has evolved into a key player in environmental conservation.
Precision agriculture exemplifies cutting-edge integration: GPS-guided tractors, drone surveillance, and AI-driven analytics enable farmers to optimize water use, fertilizer application, and harvest timing. These technologies boost yields while minimizing environmental impact, turning traditional farming into a data-rich, resource-efficient enterprise.
Yet, access remains uneven—large agribusinesses often adopt advancements faster, raising challenges around equity and rural inclusion.
Global Impact: Economies, Trade, and Food Security
Agriculture underpins global economies, contributing to over 10% of worldwide GDP and employing roughly 25% of the labor force, particularly in developing nations. Cash crops such as soybeans, cotton, and palm oil drive international trade, linking producers to consumers across continents.The Food and Agriculture Organization reports that agricultural trade generates over $1.5 trillion annually, making stability in farming systems essential to national and global economic health.
Food security remains agriculture’s most critical mission. “Every grain grown, every animal raised, every harvest preserved contributes directly to human well-being,” underscores FAO Director-General Qu Dongyu.
Yet political instability, climate change, and supply chain disruptions increasingly challenge reliable food access. Droughts in key grain-producing regions, pests like locust swarms, and trade restrictions highlight agriculture’s vulnerability and the need for resilient infrastructure and policy coordination.
- Domestic vs.
Commercial Agriculture:
Smallholder farms cultivate 80% of the world’s food but face credit, technology, and market access gaps. - Sustainable Prosperity: Investments in climate-smart agriculture promise higher productivity with lower environmental cost, balancing profit and planet.
- Trade and Geopolitics: Agricultural exports expose nations to global market volatility and diplomatic leverage.
In developing economies, agriculture often drives poverty reduction, offering rural livelihoods, income stability, and pathways out of subsistence. In developed nations, it fuels industrial and technological innovation, from biotech seeds to automated harvesting. In both contexts, agriculture shapes culture—festivals celebrate harvests, culinary traditions reflect agricultural bounty, and indigenous knowledge systems preserve centuries of adaptation.
The Future of Agriculture: Innovation, Resilience, and Responsibility
Agriculture stands at a pivotal crossroads—pressured by climate change, resource constraints, and feeding a growing population, yet rich with technological and policy innovations poised to redefine its trajectory. Champions of sustainable intensification advocate for methods that increase yields without expanding land use or degrading ecosystems. “The future farm is smarter, greener, and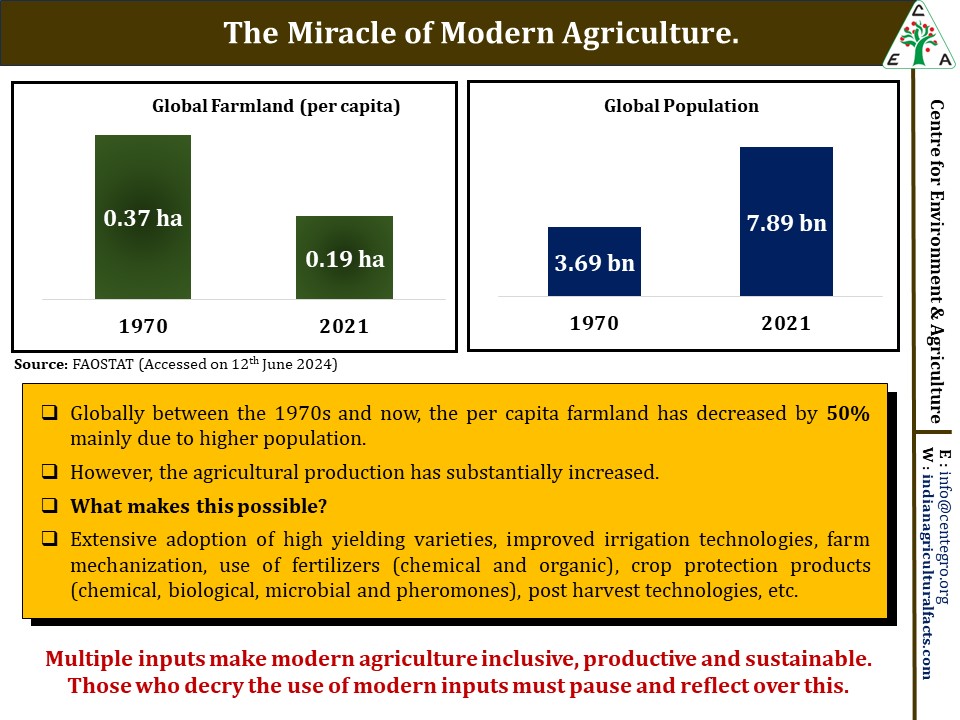



Related Post

Breaking Barriers: How Renewable Energy is Transforming American Power Systems

What Nairaland Readers Must Know: Unfiltered Insights from the Latest News Surge

Kim K’s "No Makeup" Revolution: How Minimalism, Confidence, and Authenticity Redefined Beauty

Laredo Live Pro 8 News Delivers Breakthrough Coverage of Today’s Top Stories in Real Time

